Abstract
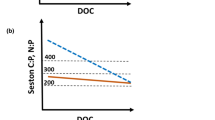
Subtropical estuaries have received comparatively little attention in the study of nutrient loading and subsequent nutrient processing relative to temperate estuaries. Australian estuaries are particularly susceptible to increased nutrient loading and eutrophication, as 75% of the population resides within 200 km of the coastline. We assessed the factors potentially limiting both biomass and production in one Australian estuary, Moreton Bay, through stoichiometric comparisons of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), silicon (Si), and carbon (C) concentrations, particulate compositions, and rates of uptake. Samples were collected over 3 seasons in 1997–1998 at stations located throughout the bay system, including one riverine endmember site. Concentrations of all dissolved nutrients, as well as particulate nutrients and chlorophyll, declined 10-fold to 100-fold from the impacted western embayments to the eastern, more oceanic-influenced regions of the bay during all seasons. For all seasons and all regions, both the dissolved nutrients and particulate biomass yielded N:P ratios <6 and N:Si ratios <1. Both relationships suggest strong limitation of biomass by N throughout the bay. Limitation of rates of nutrient uptake and productivity were more complex. Low C:N and C:P uptake ratios at the riverine site suggested light limitation at all seasons, low N:P ratios suggested some degree of N limitation and high N:Si uptake ratios in austral winter suggested Si limitation of uptake during that season only. No evidence of P limitation of biomass or productivity was evident.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Abal, E. G., W. C. Dennison, andP. T. Greenfield. 2001. Managing the Brisbane River and Moreton Bay: An integrated research/management program to reduce impacts on an Australian estuary.Water Science and Technology 43:57–70.
Abal, E. G., W. G. Dennison, andM. H. O'Donohue. 1998. Seagrasses and mangroves in Moreton Bay, p. 269–278.In I. R. Tibbetts, N. J. Hall, and W. C. Dennison (eds.), Moreton Bay and Catchment. School of Marine Science, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia.
Berg, G. M., P. M. Glibert, M. W. Lomas, andM. A. Burford. 1997. Organic nitrogen uptake and growth by the chrysophyteAureococcus anophagefferens during a brown tide event.Marine Biology 129:377–387.
Boynton, W. R., W. M. Kemp, andC. W. Keefe. 1982. A comparative analysis of nutrients and other factors influencing estuarine phytoplankton production, p. 69–90.In V. S. Kennedy (ed.), Estuarine Comparisons. Academic Press, New York.
Bronk, D. A., M. W. Lomas, P. M. Glibert, K. J. Schukert, andM. P. Sanderson. 2000. Total dissolved nitrogen analysis: Comparisons between the persulfate, UV and high temperature oxidation methods.Marine Chemistry 69:163–178.
Caperon, J. S., S. A. Cattell, andG. Krasnick. 1971. Phytoplankton kinetics in a subtropical estuary: Eutrophication.Limnology and Oceanography 16:599–607.
Caraco, N. F., J. J. Cole, P. A. Raymond, D. L. Strayer, M. L. Pace, S. E. G. Findlay, andD. T. Fischer. 1997. Zebra mussel invasion in a large, turbid river: Phytoplankton response to increased grazing.Ecology 78:588–602.
Clesceri, L. S., A. E. Greenberg, andR. R. Trussel. 1989. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 17th Edition, American Public Health Association, Washington, D.C.
Cloern, J. E. 2001. Our evolving conceptual model of the coastal eutrophication problem.Marine Ecology Progress Series 210: 223–253.
Conley, D. J., C. L. Schelske, andE. F. Stoermer. 1993. Modification of the biogeochemical cycle of silica with eutrophication.Marine Ecology Progress Series 101:179–192.
Conway, H. L., P. J. Harrison, andC. O. Davis. 1976. Marine diatoms grown in chemostats under silicate or ammonium limitation. II. Transient response ofSkeletonema costatum to a single addition of the limiting nutrientMarine Biology 35:187–199.
Costanzo, S. D., M. J. O'Donohue, W. C. Dennison, N. R. Loneragan, andM. T. Thomas. 2001. A new approach for detecting and mapping sewage impacts.Marine Pollution Bulletin 42:149–156.
Dennison, W. C. and E. Abal. 1999. Moreton Bay Study: A Scientific Basis for the Healthy Waterways Campaign. South East Queensland Regional Water Quality Management Strategy: Brisbane, Australia.
Dennison, W. C., J. M. O'Neil, E. J. Duffy, P. E. Oliver, andG. R. Shaw. 1999. Blooms of the cyanobacteriumLyngbya majuscula in coastal waters of Queensland, Australia, p. 501–506.In L. Charpy and A. W. D. Larkum (eds.), Marine Cyanobacteria. Musee Oceanographique Monaco, Monaco, France.
Dodds W. K. 2003. Misuse of inorganic N and soluble reactive P concentrations to indicate nutrient status of surface waters.Journal of the North American Benthological Society 22:171–181.
Dugdale, R. C., B. H. Jones, Jr.J. J. MacIsaac, andJ. J. Goering. 1981. Adaptation of nutrient assimilation, p. 234–250.In T. Platt (ed.), Physiological Bases of Phytoplankton Ecology. Bulletin 210, Canadian Bulletin of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, Ottawa, Canada.
Eyre, B. D. andL. J. McKee. 2002. Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus budgets for a shallow subtropical coastal embayment (Moreton Bay, Australia).Limnology and Oceanography 47: 1043–1055.
Finlayson, B. L. andT. A. McMahon. 1988. Australia vs. the world: A comparative analysis of streamflow characteristics, p. 17–40.In R. F. Warner (ed.), Fluvial Geomorphology of Australia. Academic Press, Brisbane, Australia.
Fuhrman, J. A. andF. Azam. 1982. Thymidine incorporation as a measure of heterotrophic bacterioplankton production in marine surface waters: Evaluation and field results.Marine Biology 66:109–120.
Glibert, P. M. andD. G. Capone. 1993. Mineralization and assimilation in aquatic, sediment, and wetland systems, p. 243–272.In R. Knowles and T. H. Blackburn (eds.), Nitrogen Isotope Techniques. Academic Press, San Diego, California.
Glibert, P. M., D. J. Conley, T. R. Fisher, L. W. Harding, andT. C. Malone. 1995. Dynamics of the 1995 winter/spring bloom in Chesapeake Bay.Marine Ecology Progress Series 122:27–43.
Glibert, P. M., J. Harrison, C. Heil, andS. Seitzinger. 2006. Escalating worldwide use of urea—A global change contributing to coastal eutrophication.Biogeochemistry 77:441–463.
Glibert, P. M., R. Magnien, M. W. Lomas, J. Alexander, C. Fan, E. Haramot, M. Trice, andT. M. Kana. 2001. Harmful algal blooms in the Chesapeake and coastal bays of Maryland, U.S.A.: Comparison of 1997, 1998, and 1999 events.Estuaries 24: 875–883.
Glibert, P. M., S. Seitzinger, C. A. Heil, J. M. Burkholder, M. W. Parrow, L. A. Codispoti, andV. Kelly. 2005. The role of eutrophication in the global proliferation of harmful algal blooms. Oceanography 18:198–209.
Greenwood, J., J. M. O'Neil, C. A. Heil, M. J. O'Donohue, S. Scheffers, C. Gauss, J. Greenwood, and G. Webb. 1999. Task plankton trophic dynamics (PTD). South East Queensland Regional Water Quality Strategy, Brisbane City Council, Report S2R2 No. 17. Brisbane, Australia.
Harris, G. P. 2001. Biogeochemistry of nitrogen and phosphorus in Australian catchments, rivers and estuaries: Effects of land use and flow regulation and comparisons with global patterns.Marine Freshwater Resources 52:139–149.
Heil, C. A., M. J. O'Donohue, C. A. Miller, andW. C. Dennison. 1998. Phytoplankton community response to a flood event, p. 569–584.In I. R. Tibbetts, N. J. Hall, and W. C. Dennison (eds.), Moreton Bay and Catchment, School of Marine Science, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia.
Herbland, O. 1984. Phosphorus uptake in the eutrophic layer of the equatorial Atlantic Ocean, Methodological observations and ecological significance.Oceanographie Tropicale 19:25–46.
Howarth, R., D. Anderson, J. Cloern, C. Elfring, C. Hopkinson, B. Lapointe, T. Malone, N. Marcus, K. McGlathery, A. Sharpley, andD. Walker. 2000. Nutrient pollution of coastal rivers, bays, and seas.Issues in Ecology 7:1–15.
Jassby, A. D., J. E. Cloern, andB. E. Cole. 2002. Annual primary productivity: Patterns and mechanisms of change in a nutrientrich tidal ecosystem.Limnology and Oceanography 47:698–712.
Jeffrey, S. W., D. J. Rochface, andG. R. Cresswell. 1990. Oceanography of the Australian region, p. 244–265.In M. N. Clayton and R. J. King (eds.), Biology of Marine Plants. Longman Cheshire, Melborne, Australia.
Jones, A. B., W. C. Dennison, andG. R. Stewart. 1996. Macroalgal responses to nitrogen source and availability: Amino acid metabolic profiling as a bioindicator usingGracilaria edulis (Rhodophyta).Journal of Phycology 32:757–766.
Jones, A. B., B. J. Dudley, andW. C. Dennison. 1998. Factors limiting phytoplankton biomass in the Brisbane River and Moreton Bay, p. 301–308.In I. R. Tibbetts, N. J. Hall, and W. C. Dennison (eds.), Moreton Bay and Catchment, School of Marine Science, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia.
Kemp, W. M. andW. B. Boynton. 1992. Benthic-pelagic interactions: Nutrient and oxygen dynamics, p. 149–221.In D. E. Smith, M. Leffler, and G. Mackiernan (eds.), Oxygen Dynamics in the Chesapeake Bay: A Synthesis of Research. Maryland Sea Grant College, College Park, Maryland.
Kudela, R. M. andW. P. Cochlan. 2000. Nitrogen and carbon uptake kinetics and the influence of irradiance for a red tide bloom off southern California.Aquatic Microbial Ecology 21:31–47.
Lambert, C. E. andC. A. Oviatt. 1986. Manual of Biological and Geochemical Techniques in Coastal Waters. MERL Series Report #1, 2nd edition, University of Rhode Island, Kingston, Rhode Island.
Lean, D. R. S. andC. Nalewajko. 1979. Phosphorus turnover and phosphorus demand in large and small lakes.Ergebnisse der Limnologie 13:120–132.
Lewitus, A. J., H. G. Glasgow, Jr., andJ. M. Burkholder. 1999. Kleptoplastidy in the toxic dinoflagellate,Pfiesteria piscicida (Dinophyceae).Journal of Phycology 35:303–312.
Li, Y. andT. J. Smayda. 1998. Temporal variability of chlorophyll in Narragansett Bay during an eighteen year time series.ICES Journal of Marine Science 55:661–667.
Malone, T. C., D. J. Conley, T. R. Fisher, P. M. Glibert, L. W. Harding, andK. G. Sellner. 1996. Scales of nutrient-limited phytoplankton productivity in Chesapeake Bay.Estuaries 19: 371–385.
McCarthy, J. J. andJ. L. Nevins. 1986. Utilization of nitrogen and phosphorys by primary producers in warm-core ring 82-B following deep convective mixing.Deep-Sea Research 33: 1773–1788.
McCarthy, J. J., R. W. Taylor, andJ. L. Taft. 1977. Nitrogenous nutrition of plankton of the Chesapeake Bay. 1. Nutrient availability and phytoplankton preference.Limnology and Oceanography 223:996–1011.
McComb, A. J. andJ. A. Davis. 1993. Eutrophic waters of south-western Australia.Fertiliser Research 36:105–114.
Metzler, P. M., P. M. Glibert, S. A. Gaeta, andJ. M. Ludlam. 1997. New and regenerated production in the South Atlantic off Brazil.Deep-Sea Research 44:363–384.
Moss, A. 1990. Turbidity and nutrient behaviour in the estuary, p. 307–331.In P. Davie, E. Stock, and E. Choy (eds.), In the Brisbane River, Australian Littoral Society, Brisbane, Australia.
Moss, A. 1998. Impacts of the May 1996 flood on water quality in Moreton Bay, p. 553–568.In I. R. Tibbetts, N. J. Hall, and W. C. Dennison (eds.), Moreton Bay and Catchment. School of Marine Science, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia.
Nixon, S. W. 1995. Coastal marine eutrophication: A definition, social causes, and future concerns.Ophelia 41:199–219.
Nixon, S. W., C. Oviatt, J. Frithsen, andB. Sullivan. 1986. Nutrients and the productivity of estuarine and coastal marine ecosystems.Journal of the Limnological Society of South Africa 12:43–71.
O'Donohue, M. J. H. andW. C. Dennison. 1997. Phytoplankton productivity response to nutrient concentrations, light availability and temperature along an Australian estuarine gradient.Estuaries 20:521–533.
O'Donohue, M. J. H., P. M. Glibert, andW. C. Dennison. 2000. Utilization of nitrogen and carbon by phytoplankton in Moreton Bay, Australia.Marine Freshwater Resources 51:703–712.
O'Donohue, M. J. H., C. A. Heil, S. Lowe, J. Horrocks, E. G. Abal, S. Costanzo, andW. C. Dennison. 1998. Assessing the impact of a flood event on Moreton Bay using marine plants as bioindicators of water quality, p. 585–596.In I. R. Tibbetts, N. J. Hall, and W. C. Dennison (eds.), Moreton Bay and Catchment. School of Marine Science, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia.
Paasche, E. 1980. Silicon content of five marine phytoplankton diatom species measured with a rapid filter method.Limnology and Oceanography 25:474–480.
Parsons, T. R., Y. Maita, andC. Lalli. 1984. A Manual of Chemical and Biological Methods for Seawater Analysis. Pergamon Press, London.
Perry, C. 1998. Microbial processes in seagrass sediments, Ph.D. Dissertation, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia.
Redfield, A. C., B. H. Ketchum, andF. A. Richards. 1963. The influence of organisms on the composition of sea-water, p. 26–77.In M. N. Hill (ed.), The Sea, Volume 2. John Wiley and Sons, New York.
Rivkin, R. B. andE. Swift. 1982. Phosphate uptake by the oceanic dinoflagellatePyrocystis noctiluca.Journal of Phycology 18:113–120.
Roberts, S. andW. C. Dennison. 1998. The effects of dugong grazing on seagrass communities in Moreton Bay, p. 272.In J. G. Greenwood and N. J. Hall (eds.), Proceedings of the Australial Coral Reef Society 75th Anniversary Conference, Heron Island, October 1997. School of Marine Science, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia.
Smayda, T. J. 2005. Eutrophication and phytoplankton, p. 89–98.In P. Wassmann and K. Olli (eds.), Drainage basin nutrient inputs and eutophication: An integrated approach. University of Tronso, Norway, www.ut/ee/olli/eutr/
Smil, V. 2001. Enriching the Earth: Fritz Haber, Carl Bosch, and the Transformation of World Food. The MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts.
Solárzano, L., andJ. H. Sharp. 1980. Determination of total dissolved phosphorus and particulate phosphate in natural waters.Limnology and Oceanography 25:754–758.
Stoecker, D. K., A. Li, W. Coats, D. E. Gustafson, andM. K. Nannen. 1997. Mixotrophy in the dinoflagellateProrocentrum minimum.Marine Ecology Progress Series 152:1–12.
Udy, J. W. andW. C. Dennison. 1997. Growth and physiological responses of three seagrass species to elevated sediment nutrients in Moreton Bay, Australia.Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 217:253–277.
Werner, D. 1977. Silicate metabolism, p. 110–149.In D. Werner (ed.) The Biology of Diatoms, Blackwell Scientific Publications, London.
Young, W. J., F. M. Marston, andJ. R. Davis. 1996. Nutrient exports and land use in Australian catchments.Journal of Environmental Management 47:165–183.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glibert, P.M., Heil, C.A., O'Neil, J.M. et al. Nitrogen, phosphorus, silica, and carbon in Moreton Bay, Queensland, Australia: Differential limitation of phytoplankton biomass and production. Estuaries and Coasts: J ERF 29, 209–221 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02781990
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02781990