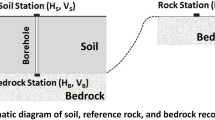
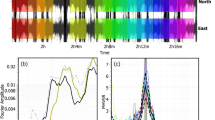
Abstract
Nakamura (Q Rep Railway Tech Res Inst 30:25–33, 1989) popularized the application of the horizontal-to-vertical spectral ratio (HVSR) analysis of microtremor (seismic noise or ambient vibration) recordings to estimate the predominant frequency and amplification factor of earthquake shaking. During the following quarter century, popularity in the microtremor HVSR (MHVSR) method grew; studies have verified the stability of a site’s MHVSR response over time and validated the MHVSR response with that of earthquake HVSR response. Today, MHVSR analysis is a popular reconnaissance tool used worldwide for seismic microzonation and earthquake site characterization in numerous regions, specifically, in the mapping of site period or fundamental frequency and inverted for shear-wave velocity depth profiles, respectively. However, the ubiquity of MHVSR analysis is predominantly a consequence of its ease in application rather than our full understanding of its theory. We present the state of the art in MHVSR analyses in terms of the development of its theoretical basis, current state of practice, and we comment on its future for applications in earthquake site characterization.

Modified from Castellaro (2016)

Original figure appears in FJ Sánchez-Sesma (2017)



(seismic section adapted from Pugin et al. 2013)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aki K (1957) Space and time spectra of stationary stochastic waves, with special reference to microtremors. Bull Earthq Res Inst 35:415–456
Albarello D, Lunedei E (2011) Structure of an ambient vibration wavefield in the frequency range of engineering interest ([0–5, 20] Hz): Insights from numerical modelling. Near Surface Geophys 9:543–559
Albarello D, Lunedei E (2013) Combining horizontal ambient vibration components for H/V spectral ratio estimates. Geophys J Int 194(2):936–951
Arai H, Tokimatsu K (1998) Evaluation of local site effects based on microtremor H/V spectra. In: Proceedings 2nd international symposium on the effects of surface geology on seismic motion, pp 673–680
Arai H, Tokimatsu K (2004) S-wave velocity profiling by inversion of microtremor H/V spectrum. Bull Seis Soc Am 94:53–63
Arai H, Tokimatsu K (2005) S-wave velocity profiling by joint inversion of microtremor dispersion curve and horizontal-to-vertical (H/V) spectrum. Bull Seismol Soc Am 95:1766–1778
Asten M, Hayashi K (2018) Application of the spatial auto-correlation method for site effect evaluation using ambient noise. Surveys Geophys (submitted)
Aylsworth JM, Lawrence DE, Guertin J (2000) Did two massive earthquakes in the Holocene induce widespread landsliding and near-surface deformation in part of the Ottawa Valley, Canada? Geology 28:903–906
Bard P-Y (1999) Microtremor measurements: a tool for site effect estimation? In: Proceedings, 2nd international symposium on the effects of surface geology on seismic motion, Yokohama, December 1998, pp 1251–1279
Bard P-Y, SESAME participants (2004) The SESAME project: an overview and main results. In: Proceedings, 13th World conference on earthquake engineering, Paper 2207
Benjumea B, Hunter JA, Burns RA, Good RL, Pullan SE (2001) Use of high-resolution shear-wave-reflection methods for determining earthquake fundamental site period response near Alfred, Ontario. Geol Surv Canada Current Research (Online) no. 2001-D3, 15 pp. https://doi.org/10.4095/212122
Benjumea B, Hunter JA, Aylsworth JM, Pullan SE (2003) Application of high-resolution seismic techniques in the evaluation of earthquake site response, Ottawa Valley, Canada. Tectonophysics 368:193–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-1951(03)00158-6
Benjumea B, Hunter JA, Pullan SE, Brooks GR, Pyne M, Aylsworth JM (2008) Vs30 and fundamental site period estimates in soft sediments of the Ottawa Valley from near-surface geophysical measurements. J Environ Eng Geophys 13(4):313–323
Benjumea B, Macau A, Gabas A, Bellmuntm F, Figueras S, Cires J (2011) Integrated geophysical profiles and H/V microtremor measurements for subsoil characterization. Near Surf Geophys 9:413–425. https://doi.org/10.3997/1873-0604.2011021
Beroya MAA, Aydin A, Tilgo R, Lasala M (2009) Use of microtremor in liquefaction hazard mapping. Eng Geol 107:140–153
Bonilla LF, Steidl JH, Lindley GT, Tumarkin AG, Archuleta RJ (1997) Site amplification in the San Fernando Valley, California: variability of site-effect estimation using the S-wave, Coda, and H/V methods. Bull Seismol Soc Am 87:710–730
Bonnefoy-Claudet S, Cotton F, Bard P-Y (2006) The nature of noise wavefield and its applications for site effects studies: a literature review. Earth Sci Rev 79:205–227
Bonnefoy-Claudet S, Köhler A, Cornou C, Wathelet M, Bard P-Y (2008a) Effects of love waves on microtremor H/V ratio. Bull Seismol Soc Am 98:288–300
Bonnefoy-Claudet S, Baize S, Bonilla LF, Berge-Thierry C, Pasten C, Campos J, Volant P, Verdugo R (2008b) Site effect evaluation in the basin of Santiago de Chile using ambient noise measurements. Geophys J Int. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2008.04020.x
Bouchon M (2003) A review of the discrete wavenumber method. Pure Appl Geophys 160:445–465
Bour M, Fouissac D, Dominique P, Martin C (1998) On the use of microtremor recordings in seismic microzonation. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 17:465–474
Castellaro S (2016) The complementarity of H/V and dispersion curves. Geophysics 81:T323–T338. https://doi.org/10.1190/geo2015-0399.1
Castellaro S, Mulargia F (2009) The effect of velocity inversions on H/V. Pure Appl Geophys 166:567–592
Castellaro S, Mulargia F (2010) How far from a building does the ground-motion free-field start? The cases of three famous towers and a modern building. Bull Seismol Soc Am 100:2080–2094
Castellaro S, Mulargia F (2014) Simplified seismic soil classification: the VfZ matrix. Bull Earthq Eng 12:735–754
Castellaro S, Panzeri R, Mesiti F, Bertello L (2015) A surface seismic approach to liquefaction. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 77:35–46
Chatelain J-L, Guillier B, Cara F et al (2008) Evaluation of the influence of experimental conditions on H/V results from ambient noise recordings. Bull Earthq Eng 6:33–74
Chiauzzi L, Cassidy JF, Kutyn K, Masi A, Mucciarelli M, Traber J, Ventura C, Yao F (2012) Estimate of the fundamental period of reinforced concrete buildings: code provisions vs experimental measures in Victoria and Vancouver (BC, Canada). In: Proceedings 15th World conference on earthquake engineering, Paper 3033, p. 10
Chiou B, Darragh R, Gregor N, Silva W (2008) NGA project strong-motion database. Earthq Spectra 24:23–44
Claerbout J (1968) Synthesis of a layered medium from its acoustic transmission response. Geophysics 33:264–269
Crow HL, Hunter JA, Motazedian D (2011) Monofrequency insitu damping measurements in Ottawa area soft soils. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 31:1669–1677
Dobry R, Oweis I, Urzua A (1976) Simplified procedures for estimating the fundamental period of a soil profile. Bull Seismol Soc Am 66:1293–1321
Endrun B (2011) Love wave contribution to the ambient vibration H/V amplitude peak observed with array measurements. J Seismol 15:443–472
Fäh D, Kind F, Giardini D (2001) A theoretical investigation of average H/V ratios. Geophys J Int 145:535–549
Fäh D, Kind F, Giardini D (2003) Inversion of local S-wave velocity structures from average H/V ratios and their use for the estimation of site effects. J Seis 7:449–467
Field E, Jacob K (1993) The theoretical response of sedimentary layers to ambient seismic noise. Geophys Res Lett 20:2925–2928
Foti S, Parolai S, Bergamo P, Di Giulio G, Maraschini M, Milana G, Picozzi M, Puglia R (2011a) Surface wave surveys for seismic site characterization of accelerometric stations in ITACA. Bull Earthq Eng 9:1797–1820
Foti S, Parolai S, Albarello D, Picozzi M (2011b) Application of surface-wave methods for seismic site characterization. Surv Geophys 32:777–825
Foti S, Hollender F, Garofalo F, Albarello D, Asten M, Bard P-Y, Comina C, Cornou C, Cox B, Di Giulio G, Forbriger T, Hayashi K, Lunedei E, Martin A, Mercerat D, Ohrnberger M, Poggi V, Renalier F, Sicilia D, Socco V (2017) Guidelines for the good practice of surface wave analysis: a product of the InterPACIFIC project. Bull Earthq Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-017-0206-7
García-Jerez A, Luzón F, Sánchez-Sesma FJ, Lunedei E, Albarello D, Santoyo MA, Almendros J (2013) Diffuse elastic wavefield within a simple crustal model: some consequences for low and high frequencies. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 118:5577–5595
García-Jerez A, Piña-Flores J, Sánchez-Sesma FJ, Luzón F, Perton M (2016) A computer code for forward computation and inversion of the H/V spectral ratio under the diffuse field assumption. Comput Geosci 97:67–78
Ghofrani H, Atkinson G (2014) Site condition evaluation using horizontal-to-vertical response spectral ratios of earthquakes in the NGA-West2 and Japanese databases. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 67:30–43
Gorstein M, Ezersky M (2015) Combination of HVSR and MASW methods to obtain shear wave velocity model of subsurface in Israel. Int J Geohazards Environ 1(1):20–41. https://doi.org/10.15273/ijge.2015.01.004
Gosar A, Lenart A (2010) Mapping the thickness of sediments in the Ljubljana Moor basin (Slovenia) using microtremors. Bull Earthq Eng 8:501–518. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-009-9115-8
Guéguen P, Cornou C, Garambois S, Banton J (2007) On the limitation of the H/V spectral ratio using seismic noise as an exploration tool: application to the Grenoble valley (France), a small apex ratio basin. Pure Appl Geophys 164:115–134
Guillier B, Atakan K, Chatelain J-L et al (2007) Influence of instruments on the H/V spectral ratios of ambient vibrations. Bull Earthq Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-007-9039-0
Guillier B, Chatelain J-L, Tavera H, Perfettini H, Ochoa A, Herrera B (2014) Establishing empirical period formula for RC buildings in Lima, Peru: evidence for the impact of both the 1974 Lima earthquake and the application of the peruvian seismic code on high-rise buildings. Seismol Res Lett 85(6):1308–1315
Hadijan AH (2002) Fundamental period and mode shape of layered soil profiles. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 22:885–891
Haghshenas E, Bard P-Y, Theodulidis N, SESAME WP04 Team (2008) Empirical evaluation of microtremor H/V spectral ratio. Bull Earthq Eng 6:75–108
Haskell NA (1960) Crustal reflection of plane SH waves. J Geophys Res 65:4147–4150
Herak M (2008) ModelHVSR: a Matlab® tool to model horizontal-to-vertical spectral ratio of ambient noise. Comput Geosci 34:1514–1526
Hinzen K-G, Weber B, Scherbaum F (2004) On the resolution of H/V measurements to determine sediment thickness, a case study across a normal fault in the Lower Rhine Embayment, Germany. J Earthq Eng 8:909–926
Hobiger M, Bard P-Y, Cornou C, Le Bihan N (2009) Single station determination of Rayleigh wave ellipticity by using the random decrement technique (RayDec). Geophys Res Lett 36:L14303. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009GL038863
Hobiger M, Cornou C, Wathelet M et al (2013) Ground structure imaging by inversions of Rayleigh wave ellipticity: sensitivity analysis and application to European strong-motion sites. Geophys J Int 192:207–229
Hunter JA, Crow HL (eds) (2012) Shear wave velocity measurement guidelines for Canadian seismic site characterization in soil and rock. Geol Surv of Canada, Open File 7078, p. 227 https://doi.org/10.4095/291753
Hunter JA, Crow HL, Brooks GR et al (2010a) Seismic site classification and site period mapping in the Ottawa area using geophysical methods. Geol Surv Canada Open File 6273, 80 p; 1 DVD. https://doi.org/10.4095/286323
Hunter JA, Burns RA, Good RL, Pullan SE, Pugin AJM, Crow H (2010b) Near-surface geophysical techniques for geohazards investigations: some Canadian examples. Lead Edge 29(8):936–947. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.3480011
Ibrahim K, Mohamed AEA, Babiker IS, Elmula AHG (2015) Local site effects evaluation for Atbara area using microtremor measurements. Am J Earth Sci 2:134–141
Ibs-von Seht M, Wohlenberg J (1999) Microtremor measurements used to map thickness of soft sediments. Bull Seismol Soc Am 89:250–259
Joyner WB, Warrick RE, Fumal TE (1981) The effect of Quaternary alluvium on strong ground motion in the Coyote Lake, California, earthquake of 1979. Bull Seismol Soc Am 71:1333–1349
Kamarudin AH, Daud ME, Ibrahim Z, Ibrahim A (2016) Sustainable non-destructive technique ambient vibrations for ground assessments. Proc Soc Behav Sci 216:701–711
Kanai K, Tanaka T (1961) On Microtremor VIII. Bull Earthq Res Inst 39:97–114
Kawase H, Sánchez-Sesma FJ, Matsushima S (2011) Application of the H/V spectral ratios for earthquake and microtremor ground motions. In: Proceedings 4th IASPEI/IAEE international symposium, effects of surface geology on seismic motion, University of California Santa Barbara
Kawase H, Matsushima S, Satoh T, Sánchez-Sesma FJ (2015) Applicability of theoretical horizontal-to-vertical ratio of microtremors based on the diffuse field concept to previously observed data. Bull Seismol Soc Am 106:3092–3103. https://doi.org/10.1785/0120150134
Köhler A, Ohrnberger M, Scherbaum F, Wathelet M, Cornou C (2007) Assessing the reliability of the modified threecomponent spatial autocorrelation technique. Geophys J Int 168:779–796
Konno K, Ohmachi T (1998) Ground-motion characteristics estimated from spectral ratio between horizontal and vertical components of microtremor. Bull Seis Soc Am 88:228–241
Lachet C, Bard P-Y (1994) Numerical and theoretical investigations on the possibilities and limitations of Nakamura’s technique. J Phys Earth 42:377–397
Le Roux O, Cornou C, Jongmans D, Schwartz S (2012) 1-D and 2-D resonances in an Alpine valley identified from ambient noise measurements and 3-D modelling. Geophys J Int 191:579–590
Lermo J, Chavez-Garcia FJ (1994) Are microtremors useful in site response evaluation? Bull Seismol Soc Am 84:1350–1364
Lévêque J-L, Maggi A, Souriau A (2010) Seismological constraints on ice properties at Dome C, Antarctica, from horizontal to vertical spectral ratios. Antarct Sci 22:572–579
Lontsi AM, Sánchez-Sesma FJ, Molina-Villegas JC, Ohrnberger M, Kruger F (2015) Full microtremor H/V(z, f) inversion for shallow subsurface characterization. Geophys J Int 202:298–312
Lunedei E, Albarello D (2015) Horizontal-to-vertical spectral ratios from a full-wavefield model of ambient vibrations generated by a distribution of spatially correlated surface sources. Geophys J Int 201:1140–1153
Macau A, Benjumea B, Gabas A, Figueras S, Vila M (2015) The effect of shallow Quaternary deposits on the shape of the H/V spectral ratio. Surv Geophys 35:185–208
Malischewsky PG, Scherbaum F (2004) Love’s formula and H/V-ratio (ellipticity) of Rayleigh waves. Wave Motion 40:57–67
Maranò S, Reller C, Loeliger H-A, Fäh D (2012) Seismic waves estimation and wavefield decomposition: application to ambient vibrations. Geophys J Int 191:175–188
Margerin L (2009) Generalized eigenfunctions of layered elastic media and application to diffuse fields. J Acoust Soc Am 125:164–174
Matsushima S, Hirokawa T, De Martin F, Kawase H, Sánchez-Sesma FJ (2014) The effect of lateral heterogeneity on horizontal-to-vertical spectral ratio of microtremors inferred from observation and synthetics. Bull Seismol Soc Am 104:381–393. https://doi.org/10.1785/0120120321
Michel C, Guéguen P, Lestuzzi P, Bard P-Y (2010) Comparison between seismic vulnerability models and experimental dynamic properties of existing buildings in France. Bull Earthq Eng 8:1295–1307
Mohamed AA, Helal AMA, Mohamed AME, Shokry MMF, Ezzelarab M (2015) Effects of surface geology on the ground-motion at New Borg El-Arab City, Alexandria, Northern Egypt. NRIAG J Astro Geophys 5:55–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nrjag.2015.11.005
Molnar S, Cassidy JF (2006) A comparison of site response techniques using weak-motion earthquakes and microtremors. Earthq Spectra 22:169–188
Motazedian D, Hunter JA, Pugin AJM, Crow H (2011a) Development of a Vs30 (NEHRP) map for the city of Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. Can Geotech J 48:458–472
Motazedian D, Khaheshi Banab K, Hunter JA, Sivathayalan S, Crow H, Brooks G (2011b) Comparison of site periods derived from different evaluation methods. Bull Seismol Soc Am 101(6):2942–2954. https://doi.org/10.1785/0120100344
Nakamura Y (1989) A method for dynamic characteristics estimation of subsurface using microtremors on the ground surface. Q Rep Railway Tech Res Inst 30:25–33
Nogoshi M, Igarashi T (1971) On the amplitude characteristics of microtremor (part 2). J Seismol Soc Japan 24:26–40
Okada H (2003) The microtremor survey method, Geophysical Monograph Series Number 12: Soc Expl Geophys, 135 p
Oliveira CS, Navarro M (2010) Fundamental periods of vibration of RC buildings in Portugal from in situ experimental and numerical techniques. Bull Earthq Eng 8:609–642
Oubaiche EH, Chatelain J-L, Bouguern A, Bensalem R, Machane D, Hellel M, Khaldaoui F, Guillier B (2012) Experimental relationship between ambient vibration H/V peak amplitude and shear-wave velocity contrast. Seismol Res Lett 83:1038–1046
Özalaybey S, Zor E, Ergintav S, Tapırdamaz MC (2011) Investigation of 3-D basin structures in the Izmit Bay area (Turkey) by single-station microtremor and gravimetric methods. Geophys J Int 186:883–894
Parolai S, Galiana-Merino JJ (2006) Effect of transient seismic noise on estimates of H/V spectral ratios. Bull Seis Soc Am 96:228–236
Parolai S, Bormann P, Milkereit C (2002) New relationships between V S, thickness of sediments, and resonance frequency calculated by the H/V ratio of seismic noise for the Cologne area (Germany). Bull Seismol Soc Am 92:2521–2527
Parolai S, Picozzi M, Richwalski SM, Milkereit C (2005) Joint inversion of phase velocity dispersion and H/V ratio curves from seismic noise recordings using a genetic algorithm, considering higher modes. Geophys Res Lett 32:L01303
Pastén C, Sáez M, Ruiz S, Leyton F, Salomón J, Poli P (2016) Deep characterization of the Santiago Basin using HVSR and cross-correlation of ambient seismic noise. Eng Geol 201:57–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.12.021
Picozzi M, Parolai S, Albarello D (2005) Statistical analysis of noise horizontal-to-vertical spectral ratios (HVSR). Bull Seismol Soc Am 95:1779–1786
Picozzi M, Strollo A, Parolai S, Durukal E, Özel O, Karabulut S, Zschau J, Erdik M (2009) Site characterization by seismic noise in Istanbul, Turkey. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 29:469–482
Pilz M, Parolai S, Leyton F, Campos J, Zschau J (2009) A comparison of site response techniques using earthquake data and ambient seismic noise analysis in the large urban areas of Santiago de Chile. Geophys J Int 178:713–728. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04195.x
Piña-Flores J, Perton M, García-Jerez A, Carmona E, Luzón F, Molina-Villegas JC, Sánchez-Sesma FJ (2017) The inversion of spectral ratio H/V in a layered system using the diffuse field assumption (DFA). Geophys J Int 208:577–588
Poggi V, Fäh D (2010) Estimating Rayleigh wave particle motion from three-component array analysis of ambient vibrations. Geophys J Int 180:251–267
Poggi V, Fäh D, Burjanek J, Giardini D (2012) The use of Rayleigh wave ellipticity for site-specific hazard assessment and microzonation: application to the city of Lucerne, Switzerland. Geophys J Int 188:1154–1172
Pugin AJM, Brewer K, Cartwright T, Pullan SE, Perret D, Crow HL, Hunter JA (2013) Near surface S-wave seismic reflection profiling—new approaches and insights. First Break EAGE 31:49–60. https://doi.org/10.3997/1365-2397.2013005
Rošer J, Gosar A (2010) Determination of VS30 for seismic ground classification in the Ljubjana area, Slovenia. Acta Geotech Slov 1:61–76
Roten D, Fäh D, Cornou C, Giardini D (2006) Two-dimensional resonances in Alpine valleys identified from ambient vibration wavefields. Geophys J Int 165:889–905
Salameh C, Guillier B, Harb J, Cornou C, Bard P-Y, Voisin C, Mariscal A (2016) Seismic response of Beirut (Lebanon) buildings: instrumental results from ambient vibrations. Bull Earthq Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-016-9920-9
Sánchez-Sesma FJ (2017) Modeling and inversion of the microtremor H/V spectral ratio: physical basis behind the diffuse field approach. Earth Planets Space 69:92
Sánchez-Sesma FJ, Rodríguez M, Iturrarán-Viveros U, Luzón F, Campillo M, Margerin L, García-Jerez A, Suárez M, Santoyo MA, Rodríguez-Castellanos A (2011) A theory for microtremor H/V spectral ratio: application for a layered medium. Geophys J Int 186(1):221–225
SESAME et al. (2004) Guidelines for the implementation of the H/V spectral ratio technique on ambient vibrations: measurements, processing, and interpretation. SESAME European research project, WP12—Deliverable D23.12
Seyhan E, Stewart JP, Ancheta TD, Darragh RB, Graves RW (2014) NGA-West 2 site database. Earthq Spectra 30:1007–1024
Socco LV, Strobbia C (2004) Surface wave methods for near-surface characterization: a tutorial. Near Surf Geophys 2:165–185
Tuan TT, Scherbaum F, Malischewsky PG (2011) On the relationship of peaks and troughs of ellipticity (H/V) of Rayleigh waves and the transmission response of single layer over half-space models. Geophys J Int 184:793–800
Uebayashi H (2003) Extrapolation of irregular subsurface structures using the horizontal-to-vertical spectral ratio of long-period microtremors. Bull Seismol Soc Am 93:570–582
Uebayashi H, Kawabe H, Kamae K (2012) Reproduction of microseism H/V spectral features using a three-dimensional complex topographical model of the sediment-bedrock interface in the Osaka sedimentary basin. Geophys J Int 189:1060–1074. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2012.05408.x
Van der Baan M (2009) The origin of SH-wave resonance frequencies in sedimentary layers. Geophys J Int 178:1587–1596
Woolery EW, Street R (2002) 3D near-surface soil response from H/V ambient-noise ratios. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 22:865–876
Yamamoto H (2000) Estimation of shallow S-wave velocity structures from phase velocities of Love-and Rayleigh-waves in microtremors. In: Proceedings of the 12th World conference on earthquake engineering
Yañez G, Muñoz M, Flores-Aqueveque V, Bosch A (2015) Gravity derived depth to basement in Santiago Basin, Chile: implications for its geological evolution, hydrogeology, low enthalpy geothermal, soil characterization and geo-hazards. Andean Geol 42:190–212
Yong A, Martin A, Stokoe K, Diehl J (2013) ARRA-funded VS30 measurements using multi-technique approach at strong-motion stations in California and central-eastern United States: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2013–1102, 60p. and data files http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2013/1102
Zor E, Özalaybey S, Karaaslan A, Tapırdamaz MC, Özalaybey SÇ, Tarancıoglu A, Erkan B (2010) Shear wave velocity structure of the Izmit Bay area (Turkey) estimated from active–passive array surface wave and single-station microtremor methods. Geophys J Int 182:1603–1618
Acknowledgements
Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the Consortium of Organizations for Strong-Motion Observation Systems (COSMOS) Facilitation Committee for the Development of the COSMOS International Guidelines for the Application of Noninvasive Geophysical Techniques to Characterize Seismic Site Conditions. Any use of trade, firm, or product names is for descriptive purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the US Government. Thanks are given to J. Piña-Flores for his comments and suggestions and to G. Sánchez, E. Plata, and their team of the Unidad de Servicios de Información (USI) of the Institute of Engineering-UNAM for locating useful references. Partial support by AXA Research Fund, by DGAPA-UNAM under Project IN100917 is gratefully acknowledged. Natural Resources Canada (Geological Survey of Canada) gratefully acknowledges the contributions of Dr. André Pugin in the processing of the seismic section produced herein, and the support of the Public Safety Geoscience and Groundwater Geoscience Programs. This is ESS Contribution number 20170132. This paper was improved from U.S. Geological Survey reviews by Drs. Stephen Hartzell and William Stephenson.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molnar, S., Cassidy, J.F., Castellaro, S. et al. Application of Microtremor Horizontal-to-Vertical Spectral Ratio (MHVSR) Analysis for Site Characterization: State of the Art. Surv Geophys 39, 613–631 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-018-9464-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-018-9464-4