Abstract
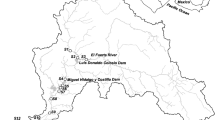
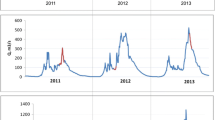
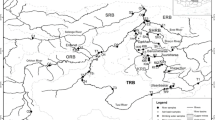
The Saigon River, Southern Vietnam, crosses one of the most dynamic developing Megacity in Southeast Asia: Ho Chi Minh City (HCMC). The increased economic, industrial, and domestic developments may affect the environmental quality of water and halieutic resources. In this study, we evaluated the seasonal (dry and wet seasons) biogeochemical state of the Saigon River during two snapshot campaigns conducted along the river basin upstream from HCMC; the Saigon River was characterized by slightly acidic (pH 5.7–7.7) and oxygen-depleted water (dissolved oxygen (DO), 0.36–5.18 mg l−1). Nutrients (N–NH4 = 0.01–2.41, N–NO3 = 0.14–2.72, and P–PO4 = ~0–0.42 mg l−1), DOC (2.2–8.0 mg l−1), POC, and trace metal(oid) (As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Zn, and Hg) concentrations were low showing a good quality of the upstream river. In the urban center area, DO dropped to 0.03 mg l−1 accompanied with a rise of nutrient concentrations (e.g., N–NH4, up to 17.7 mg l−1) likely originating from wastewater discharges. Trace metal concentrations also rose sharply (e.g., Cr and Hg rose up to 10-fold higher) in both water and sediments but remained under the World Health Organization (WHO) and Vietnamese concentration guidelines. In the downstream estuarine area, the intrusion of marine waters diluted water flowing from HCMC, leading water quality to return close to the state observed upstream from HCMC. In general, levels of nutrient and metal contaminations along the Saigon River during both seasons appear moderate regarding to Vietnamese and WHO guidelines although the urban area is highlighted as the major contributor for metal(oid) emissions. Finally, we showed that apart from wastewater and industrial discharges that affect the river quality, metal(oid) partitioning between solid and solution is controlled by the change in water geochemistry along the continuum during both seasons, such as DO (e.g., for As and Cr) and pH (e.g., for Pb) which drives their sorption/dissolution dynamics.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aminot A and Kerouel R (2004). Hydrologie des écosystèmes marins. Paramètres et analyses. Edition Ifremer.
Anh MB, Hong LCD, Nguyen NV, Thi CLT, Minh TL, Becker-Van Slooten K, Tarradellas J (2003) Micropollutants in the sediment of the SaiGon–DongNai River: situation and ecological risks. Chimia 57:537–541
APHA 1995. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, American Public Health Association. Washington, DC
Apitz SE, Power EA (2002) From risk assessment to sediment management: an international perspective. J. Soils Sediments 2:61–66
Aspila KI, Agemian H, Chau ASY (1976) A semi-automated method for the determination of inorganic, organic and total phosphate in sediments. Analyst 10:1187–1197
Audry S, Blanc G, Schäfer J, Chaillou G, Robert S (2006) Early diagenesis of trace metals (Cd, Cu, Co, Ni, U, Mo, and V) in the freshwater reaches of a macrotidal estuary. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70:2264–2282
Balogh SJ, Nollet YH (2008) Methylmercury input to the Mississippi River from a large metropolitan wastewater treatment plant. Sci Tot Environ 406:145–153
Balogh SJ, Swain EB, Nollet YH (2006) Elevated methylmercury concentrations and loadings during flooding in Minnesota rivers. Sci Tot Environ 368:138–148
Benoit JM, Gilmour C, Mason R, Heyes A (1999) Sulfide controls on mercury speciation and bioavailability to methylating bacteria in sediment pore waters. Environ Sci Technol 33:951–957
Benoit JM, Gilour CC, Heyes A, Mason RP, Miller CL (2003) Geochemical and biological controls over methylmercury production and degradation in aquatic ecosystems. In: Cai Y, Braids OC (eds) Biochemistry of environmentally important trace elements. ACS symposium series 835. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp. 262–297
Berg M, Trang PTK, Stengel C, Buschmann J, Viet PH, Dan VN, Giger W, Stüben D (2008) Hydrological and sedimentary controls leading to arsenic contamination of groundwater in the Hanoi area, Vietnam: the impact of iron-arsenic ratios, peat, river bank deposits, and excessive groundwater abstraction. Chem Geol 249:91–112
Bloom NS, Fitzgerald WF (1988) Determination of volatile mercury species at the picogram level by low-temperature gas chromatography with cold-vapor atomic fluorescence detection. Anal Chim Acta 208:151–161
Boyle E, Collier R, Dengler AT, Edmond JM, Ng AC, Stallard RF (1974) On the chemical mass-balance in estuaries. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 38:1719–1728
Bravo AG, Bouchet S, Guédron S, Amouroux D, Dominik J, Zopfi J (2015) High methylmercury production under iron-reducing conditions in sediments impacted by sewage treatment plant discharges. Wat Res 80:245–2552015
Campbell JA, Yeats PA (1984) Dissolved chromium in the St. Lawrence estuary. Estuar Coast Shelf S 19:513–522
Castelle S, Schafer J, Blanc G, Audry S, Etcheber H, Lissalde JP (2007) 50-year record and solid state speciation of mercury in natural and contaminated reservoir sediment. Appl Geochem 22:1359–1370
Censi RM, Martin JM (2004) Concentration and fate of trace metals in Mekong River Delta. Sc Tot Environ 332:167–182
Chanpiwat P, Sthiannopkao S (2013) Status of metal levels and their potential sources of contamination in southeast Asian rivers. Environ Sci Pollut Res. doi:10.1007/s11356-013-1858-8
Chiffoleau JF, Cossa D, Auger D, Truquet I (1994) Trace metal distribution, partition and fluxes in the seine estuary (France) in low discharge regime Spatio. Mar Chem 47:145–158
Comans RNJ, van Dijk CPJ (1988) Role of complexation processes in cadmium mobilization during estuarine mixing. Nature 336:151–154
Conley DJ, Paerl HW, Howarth RW, Boesch DF, Seitzinger SP, Havens KE, Lancelot C, Likens GE (2009) Controlling eutrophication: nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 323:1014–1015
Cossa D, Gobeil C (2000) Mercury speciation in the lower St. Lawrence estuary. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 57:138–147
Cossa D, Mason RP, Fitzgerald WF (2006) Chemical speciation of mercury in a Meromictic lake. In: WC J, HJ W (eds) Mercury pollution: integration and synthesis. CRC Press, Inc., pp. 57–67
Coulthart A, Quang N, Sharpe H (2006) Urban development strategy. Meeting the challenges of rapid urbanization and the transition to a market oriented economy (Monograph). World Bank, Hanoi, Vietnam
Dabrin A, Schäfer J, Blanc G, Strady E, Masson M, Bossy C, Castelle S, Girardot N, Coynel A (2009) Improving estuarine net flux estimates for dissolved cadmium export at the annual timescale: application to the Gironde estuary. Estuar Coast Shelf S 84:429–439
Dan NP, Ha NTV, Thanh BX, Khoa HL (2007). Water resources management in Ho Chi Minh City. Institute for Global Environmental Strategies IGES report, Kanagawa, Japan. http://pub.iges.or.jp/modules/envirolib/upload/981/attach/00_complete_report.pdf
Datta DK, Subramanian V (1998) Distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in the surface sediments of the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna river system in the Bengal basin. Environ Geol 36:93–101
Etcheber H, Relexans JC, Beliard M, Weber O, Buscail R, Heussner S (1999) Distribution and quality of sedimentary organic matter on the Aquitanian margin (Bay of Biscay). Deep-Sea Res Part II 46:2249–2288
Evans AEV, Hanjra MA, Jiang Y, Qadir M, Drechsel P (2012) Water quality: assessment of the current situation in Asia. Int J WaterResour Dev 28:195–216
Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO) (2014). Aquastat: Global information system on water and agriculture. http://www.fao.org/nr/water/aquastat/data/cf/readPdf.html?f=VNM-CF_eng.pdf
Förstner U, Salomons W (2008) Trends and challenges in sediment research: the role of sediments in river basin management. J Soils Sed 8:281–283
Gaillardet J, Dupré B, Allegre CJ (1999) Geochemistry of large river suspended sediments: silicate weathering or crustal recycling? Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63:4037–4051
Garnier J, Billen G, Cébron A (2007) Modelling nitrogen transformations in the lower Seine river and estuary (France): impact of wastewater release on oxygenation and N2O emission. Hydrobiol 588:291–302
Garnier J, Billen G, Némery J, Sebilo M (2010) Transformations of nutrients (N, P, Si) in the turbidity maximum zone of the Seine estuary and export to the sea. Est Coast Shelf Sc 90:129–141
General Statistics Office of Vietnam (GSO) (2014). Statistical yearbook of Ho Chi Minh City—2013, Ho Chi Minh City Statistical Office.
Givental E (2014) The Ho Chi Minh City canals: assessing vulnerability and resilience factors. Association of Pacific Coast Geographers Yearbook 76:49–67
Guédron S, Duwig C, Prado BL, Point D, Flores MG, Siebe C (2014a) (Methyl)mercury, arsenic, and lead contamination of the World’s largest wastewater irrigation system: the Mezquital Valley (Hidalgo State-Mexico). Water Air Soil Poll 225:–2045
Guédron S, Grangeon S, Lanson B, Grimaldi M (2009) Mercury speciation in a tropical soil association; consequence of gold mining on Hg distribution in French Guiana. Geoderma 153:331–346
Guédron S, Tisserand D, Garambois S, Spadini L, Molton F, Bounvilay B (2014b) Baseline investigation of (methyl)mercury in waters, soils, sediments and key foodstuffs in the lower Mekong Basin: the rapidly developing city of Vientiane (Lao PDR). J Geochem Explor 143:96–102
Huy NQ, Luyen TV, Phe TM, Mai NV (2003) Toxic elements and heavy metals in sediments in Tham Luong Canal, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Environ Geol 43:836–841
Islam MS, Ahmed MK, Raknuzzaman M, Al-Mamun MH, Islam MK (2015) Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: a preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecol Indicat 48:282–291
Jacobs L, Emerson S (1982) Trace metal solubility in an anoxic fjord. Earth Planet Sci Let 60:237–252
Jeffrey SW (1980) Algal pigment systems. In: Falkowski PG (ed) Primary productivity in the sea. Plenum, New York, pp. 33–58
Lohring DH (1991) Normalization of heavy-metal data from estuarine and coastal sediments. ICES J Mar Sc 48:101–115
Luu TNM, Garnier J, Billen G, Le TPQ, Nemery J, Orange D, Le LA (2010) N, P, Si budgets for the Red River Delta (northern Vietnam): how the delta affects river nutrient delivery to the sea. Biogeochem 107:241–259
Marcotullio PJ (2007) Urban water-related environment transitions in Southeast Asia. Sustain Sci 2:27–54
Meybeck M (2013) Heavy metal contamination in rivers across the globe: an indicator of complex interactions between societies and catchments. In: Proceeding of H04, IAHS-IAPSO-IASPEI Assembly, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2013.
Meybeck M, Lestel L, Bonte P, Moilleron R, Colin J, Rousselot O, Herve D, De Ponteves C, Groisbois C, Thevenot D (2007) Historical perspectives of heavy metal contamination (Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Pb, Zn) in the seine river basin (France) following a DPSIR approach (1950–2005). Sci Total Environ 375:204–231
Meybeck M, Roussenac S, Dürr H, Vogler J (2005) Lateral carbon transport in freshwaters. CarboEurope Cluster report, 55 p.
Minh NH, Minh TB, Iwata H, Kajiwara N, Kunisue T, Takahashi S, Viet PH, Tuyen BC, Tanabe S (2007) Persistent organic pollutants in sediments from Sai Gon-Dong Nai River basin, Vietnam: levels and temporal trends. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 52:458–465
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chimica Acta 27:31–36
Némery J, Garnier J (2007) Origin and fate of phosphorus in the seine watershed (France): the agricultural and hydrographic P budget. J Geo Res Biogeosci 112
Nguyen TVH, Takizawa S, Oguma K, Nguyen VP (2011) Sources and leaching of manganese and iron in the Saigon River Basin, Vietnam. Water Sc Techno 63:2231–2237
Parker JL, Bloom NS (2005) Preservation and storage techniques for low-level aqueous mercury speciation. Sc Total Environ 337:253–263
Patterson CC, Settle DM (1976) The reduction of orders of magnitude errors in lead analyses of biological materials and natural waters by evaluating and controlling the extent and sources of industrial lead contamination introduced during sample collecting, handling, and analysis. Natl Bureau Stand Special Publ 422:321–351
Phuong PK, Son CPN, Sauvain JJ, Tarradellas J (2008) Contamination by PCB’s, DDT’s, and heavy metals in sediments of Ho Chi Minh City’s canals, Viet Nam. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 60:347–354
QCVN (2008) QCVN 08:2008/BTNMT, National Technical Regulation on Surface Water Quality, Hanoi, Vietnam.
Rang MC, Kleijn CE, Schouten CJ (1986) Historical changes in the enrichment of fluvial deposits with heavy metals. Int Assoc Hydrol Sci Publ 157:47–59
Sajor EE, Thu NM (2009) Institutional and development issues in integrated water resource management of Saigon River. J Envir Devel 1:268–290
Sonke JE, Schäfer J, Chmeleff J, Audry S, Blanc G, Dupré B (2010) Sedimentary mercury stable isotope records of atmospheric and riverine pollution from two major European heavy metal refineries. Chem Geol 279:90–100
Sugimura Y, Suzuki Y (1988) A high temperature catalytic oxidation method for non-volatile dissolved organic carbon in seawater by direct injection of a liquid sample. Mar Chem 24:105–131
Svendsen LM, Redsdorf A, Nørnberg P (1993) Comparison of methods for analysis of organic and inorganic phosphorus in river sediment. Water Res 27:77–83
Thuy HTT, Nguyen NHV, Tu TCL (2007) Anthropogenic input of selected heavy metals (Cu, Cr, Pb, Zn and Cd) in the aquatic sediments of Hochiminh City, Vietnam. Water Air Soil Poll 182:73–81
Trinh AD, Giang NH, Vachaud G, Choi SU (2009) Application of excess carbon dioxide partial pressure (EpCO2) to the assessment of trophic state of surface water in the Red River Delta of Vietnam. Int J Environ Stud 66:27–47
Trinh AD, Meysman F, Rochelle-Newall E, Bonnet MP (2012) Quantification of sediment-water interactions in a polluted tropical river through biogeochemical modeling. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 26:GB3010. doi:10.1029/2010GB003963
Trinh AD, Vu DL, Ta TT (2013) Partition of heavy metals in a tropical river system impacted by municipal waste. Environ Monit Assess 185:1907–1925
Turner A (1996) Trace-metal partitioning in estuaries: importance of salinity and particle concentration. Mar Chem 54:27–39
Turner A, Millward GE, Bale AJ, Morris AW (1993) Application of the KD concept to the study of trace metal removal and desorption during estuarine mixing. Estuar Coast Shelf S 36:1–13
Turner DR, Whitfield M, Dickson AG (1981) The equilibrium speciation of dissolved components in freshwater and seawater at 25 °C and 1 atm pressure. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 45:855–881
van Leeuwen CJ, Nguyen PD, Dieperink C (2015) The challenges of water governance in Ho Chi Minh City. SETAC 2015. Integr Environ Assess Manag 9999:1–8
Viers J, Dupré B, Gaillardet J (2009) Chemical composition of suspended sediments in world rivers: new insights from a new database. Sci Total Envir 407:853–868
Vo PL (2007) Urbanization and water management in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam—issues, challenges and perspectives. GeoJ 70:75–89
Wedepohl H (1995) The composition of the continental crust. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 59:1217–1232
Wetzel RG (1983) Limnology, 2nd edn. Saunders College Publishing, Philadelphia, 860 pp
WHO (2011) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, fourth Eds, 564p. Organization, World Health
Wijaya AR, Ouchi AK, Tanaka K, Cohen MD, Sirirattanachai S, Shinjo R, Ohde S (2013) Evaluation of heavy metal contents and Pb isotopic compositions in the Chao Phraya River sediments: implication for anthropogenic inputs from urbanized areas, Bangkok. J Geoch Explor 126-127:45–54
World Bank (2012). Vietnam-Ho Chi Minh City Environmental Sanitation (Nhieu Loc-Thi Nghe Basin) Project.Washington,DC:WorldBank.http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/2012/12/17151849/vietnam-ho-chi-minh-city-environmental-sanitation-nhieu-loc-thi-nghe-basin-project
Zhang J, Liu CL (2002) Riverine composition and estuarine geochemistry of particulate metals in China: weathering features, anthropogenic impact and chemical fluxes. Estuar Coast Shelf S 54:1051–1070
Acknowledgments
This study has been conducted under the framework of CARE-RESCIF initiative. The authors would like to thank the students for their help during sampling. This study was funded by incentive grants from Institut de Recherche pour le Développement IRD, by AGIR grants from Grenoble Alpes University, by grants from the Vietnam National University (grant number B2016-20-05), and by grants from Region Rhônes Alpes COOPERA “Take Care.” LTHE is part of Labex OSUG@2020 (ANR10 LABX56).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strady, E., Dang, V.B.H., Némery, J. et al. Baseline seasonal investigation of nutrients and trace metals in surface waters and sediments along the Saigon River basin impacted by the megacity of Ho Chi Minh (Vietnam). Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 3226–3243 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7660-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7660-7