Abstract.
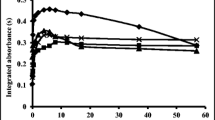
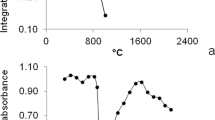
A flow injection hydride generation graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometric (FI-HG-GFAAS) method was applied to the determination of Se in Se-doped and undoped cereals and bakery products. For the purpose of doping, the soils used for the cultivation of the cereals were dosed with Se-doped foliar fertilizers. The samples were dissolved in a mixture of HNO3 and H2O2 solutions using microwave-assisted digestion. The decomposition of H2Se generated from the sample solutions and the trapping of elemental Se were performed at a temperature of 300 °C on an Ir-pretreated integrated graphite platform of a transversally heated graphite atomizer (THGA). For release of the trapped Se within a fairly short atomization time (5 s), an atomization temperature of 2200 °C was observed to be optimal. The overall efficiency of hydride generation, transport and trapping was ∼86%.
The upper limit of the linear dynamic range of calibration was 10 µg L−1, which corresponds to 0.5 µg g−1 for solid samples. Recovery of the samples spiked with SeVI solutions was found to be 93±6% on average. The relative standard deviation of the determinations was less than 8%. The limit of detection was found to be 0.06 µg L−1, corresponding to 3 ng g−1 for solid samples. The accuracy of the method was verified with the use of IAEA-155 (whey powder) certified reference material. End-capped THGA tubes resulted in an extension of the linear calibration range compared to that of standard THGAs.
The Se content in bakery products made of undoped cereals ranged from 7.7 to 68 ng g−1 (wet weight) in 18 samples, whereas the Se content of the corresponding cereals was found to be below 100 ng g−1 (wet weight). The Se level of cereals grown on soils treated with Se-doped fertilizers ranged from 128 to 1046 ng g−1 (wet weight), and it depended linearly on the Se concentration of the corresponding foliar fertilizer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ajtony, Z., Szoboszlai, N., Bella, Z. et al. Determination of Total Selenium Content in Cereals and Bakery Products by Flow Injection Hydride Generation Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometry Applying in-situ Trapping on Iridium-Treated Graphite Platforms. Microchim Acta 150, 1–8 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-005-0330-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-005-0330-y