Abstract
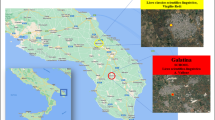
The promotion of good indoor air quality in schools is of particular public concern for two main reasons: (1) school-age children spend at least 30% of their time inside classrooms and (2) indoor air quality in urban areas is substantially influenced by the outdoor pollutants, exposing tenants to potentially toxic substances. Two schools in Curitiba, Brazil, were selected to characterize the gaseous compounds indoor and outdoor of the classrooms. The concentrations of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and the isomers xylenes (BTEX); NO2; SO2; O3; acetic acid (HAc); and formic acid (HFor) were assessed using passive diffusion tubes. BTEX were analyzed by gas chromatography–ion trap mass spectrometry and other collected gasses by ion chromatography. The concentration of NO2 varied between 9.5 and 23 µg m−3, whereas SO2 showed an interval from 0.1 to 4.8 µg m−3. Within the schools, BTEX concentrations were predominant. Formic and acetic acids inside the classrooms revealed intermediate concentrations of 1.5 µg m−3 and 1.2 µg m−3, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arts, J. H. E., Muijser, H., Kuper, C. F., & Woutersen, R. A. (2008). Setting an indoor air exposure limit for formaldehyde: Factors of concern. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 52, 189–194.
Ashmore, M. R., & Dimitroulopoulou, C. (2009). Personal exposure of children to air pollution. Atmospheric Environment, 43, 128–141.
Avigo, D., Jr., Godoi, A. F. L., Janissek, P. R., Makarovska, Y., Krata, A., Potgieter-Vermaak, S., et al. (2008). Particulate matter analysis at elementary schools in Curitiba, Brazil. Analytical Bioanalytical Chemistry, 391, 1459–1468.
Bertoni, G., Ciuchini, C., Pasini, A., & Tappa, R. (2002). Monitoring of ambient BTX at Monterotondo (Rome) and indoor–outdoor evaluation in school and domestic sites. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 4, 903–909.
Burt, P. J. A., & Sharma, P. (2002). Effects of aeroallergens on the lung function of primary school children at two contrasting sites in South-East England. Aerobiologia, 18, 125–134.
Cocheo, V., Boaretto, C., & Sacco, P. (1996). High uptake rate radial diffusive sampler suitable for both solvent and thermal desorption. American Industrial Hygiene Association Journal, 57, 897–904.
Godoi, R. H. M., Braga, D. M., Makarovska, Y., Alfoldy, B., Carvalho, M. A. S., Van Grieken, R., Godoi, A. F. L. (2008). Inhable particulate matter from lime industries: Chemical composition and deposition in human respiratory tract. Atmospheric Environment, 42(30), 7027–7033.
Godoi, R. H. M., Godoi, A. F. L., Worobiec, A., Andrade, S. J., de Hoog, J., Santiago-Silva, M. R., Van Grieken, R. (2004). Characterisation of sugar cane combustion particles in the Araraquara region, Southeast Brazil. Microchimica Acta, 145(1–4), 53–56.
Godoi, R. H. M., Kontozova, V., Van Grieken, R. (2006). The shielding effect of the protective glazing of historical stained glass windows from an atmospheric chemistry perspective: Case study Sainte Chapelle, Paris. Atmospheric Environment, 40(7), 1255–1265.
Godoi, A. F. L., Sawada, E. Y., de Marchi, M. R. R., Van Grieken, R., & Godoi, R. H. M. (2009). Determination of BTEX by GC-MS in air of offset printing plants: comparison between conventional and ecological inks. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution: Focus. doi:10.1007/s11267-009-9219-9.
Guieysse, B., Hort, C., Platel, V., Munoz, R., Ondarts, M., & Revah, S. (2008). Biological treatment of indoor air for VOC removal: Potential and challenges. Biotechnology Advances, 26(5), 398–410.
Guo, H., Lee, S. C., Li, W. M., & Cao, J. J. (2003). Source characterisation of BTEX in indoor microenvironments in Hong Kong. Atmospheric Environment, 37, 73–82.
Japan Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Committee on sick house syndrome: Indoor air pollution progress. Report No.1—Summary on the discussions from the 1st to 3rd meeting, 2000, Tokyo. http://www.nihs.go.jp/mhlw/chemical/situnai/kentoukai/rep-eng1.pdf#search¼’Japanese indoor air guideline, 2000.
Jacobson, M. (2007). Effects of ethanol (E85) versus gasoline vehicles on cancer and mortality in the United States. Environmental Science & Technology, 41, 4150–4157.
Kampa, M., & Castanas, E. (2008). Human health effects of air pollution. Environmental Pollution, 151, 362–367.
Kim, J. J., Smorodinsky, S., Lipsett, M., Singer, B. C., Hodgson, A. T., & Ostro, B. (2004). Traffic-related air pollution near busy roads. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 170, 520–526.
Kotzias, D., Koistinen, K., Kephalopoulos, S., Schlitt, C., Carrer, P., Maroni, M., et al. (2005). The INDEX project. Critical appraisal of the setting and implementation of indoor exposure limits in the EU (pp. 1–50). Ispra: European Commission, Institute for Health and Consumer Protection, Physical and Chemical Exposure Unit. 275–281.
Latza, U., Gerdes, S., & Baur, X. (2009). Effects of nitrogen dioxide on human health: Systematic review of experimental and epidemiological studies conducted between 2002 and 2006. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 212, 271–287.
Lee, S. C., & Chang, M. (2000). Indoor and outdoor air quality investigation at schools in Hong Kong. Chemosphere, 41, 109–113.
Lovreglio, P., Carrus, A., Iavicoli, S., Drago, I., Persechino, B., & Soleo, L. (2009). Indoor formaldehyde and acetaldehyde levels in the province of Bari, South Italy, and estimated health risk. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 11, 955–961.
Madureira, J., Alvim-Ferraz, M. C. M., Rodrigues, S., Gonçalves, C., Azevedo, M. C., Pinto, E., et al. (2009). Indoor air quality in schools and health symptoms among Portuguese teachers. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 15, 159–169.
Maynard, R. L. (1997). 1997 NSCA Pollution Handbook: The Essential Guide to UK and European Pollution Control Legislation. Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 54, 624.
Mendell, M. J., & Heath, G. A. (2004). Do indoor pollutants and thermal conditions in schools influence student performance? A critical review of the literature. Indoor Air, 15, 27–52.
Pearson, R. L., Wachtel, H., & Ebi, K. L. (2000). Distance-weighted traffic density in proximity to a home is a risk factor for leukemia and other childhood cancers. Journal of the Air and Waste Management Association, 50, 175–180.
Pilotto, L. S., Douglas, R. M., Attewell, R. G., & Wilson, S. R. (1997). Respiratory effects associated with indoor nitrogen dioxide exposure in children. International Journal of Epidemiology, 26, 788–796.
Pinto, J. P., & Solci, M. C. (2007). Comparison of rural and urban atmospheric aldehydes in Londrina, Brazil. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 18, 928–936.
Ruchirawat, M., Navasumrit, P., Settachan, D., Tuntaviroon, J., Buthbumrung, N., & Sharma, S. (2005). Measurement of genotoxic air pollutant exposures in street vendors and school children in and near Bangkok. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 206, 207–214.
Rusznak, C., Devalia, J. L., & Davies, R. J. (1994). The impact of pollution on allergic disease. Allergy, 49, 21–27.
Stranger, M. (2005) PhD thesis. Characterisation of health related particulate and gas-phase compounds in multiple indoor and outdoor sites in Flanders. Micro- and Trace Analysis Centre (MiTAC) in the Department of Chemistry, University of Antwerp.
Stranger, M., Potgieter-Vermaak, S. S., & Van Grieken, R. (2007). Comparative overview of indoor air quality in Antwerp, Belgium. Environment International, 33, 789–797.
Stranger, M., Potgieter-Vermaak, S. S., Sacco, P., Quaglio, F., Pagani, D., Cocheo, C., et al. (2008a). Analysis of indoor gaseous formic and acetic acid, using radial diffusive samplers. Journal of Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 149, 411–417.
Stranger, M., Potgieter-Vermaak, S. S., & Van Grieken, R. (2008b). Characterisation of indoor air quality in primary schools in Antwerp, Belgium. Indoor Air, 18, 454–463.
WHO. (2000). Air quality guidelines for Europe. 2nd ed. Copenhagen, World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe, 2000 (WHO Regional Publications, European Series No. 91).
WHO. (2005). WHO Air quality guidelines for particulate matter, ozone, nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide—Global Update 2005. Summary of Risk Assessment. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO Press.
Yanowitz, J., & McCormick, R. L. (2009). Effect of E85 on tailpipe emissions from light-duty vehicles. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 59, 172–182.
Zhao, Z., Zhang, Z., Wang, Z., Ferm, M., Liang, Y., & Norbäck, D. (2008). Asthmatic symptoms among pupils in relation to winter indoor and outdoor air pollution in schools in Taiyuan, China. Environmental Health Perspectives, 116, 90–97.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Godoi, R.H.M., Avigo, D., Campos, V.P. et al. Indoor Air Quality Assessment of Elementary Schools in Curitiba, Brazil. Water Air Soil Pollut: Focus 9, 171–177 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11267-009-9220-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11267-009-9220-3