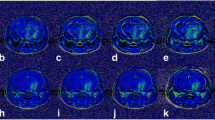
BSA-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles with different hydrodynamic diameters (36±4 and 85±10 nm) were synthesized, zeta potential and T2 relaxivity were determined, and their morphology was studied by transmission electron microscopy. Studies on rats with experimental glioma C6 showed that smaller nanoparticles more effectively accumulated in the tumor and circulated longer in brain vessels. Optimization of the hydrodynamic diameter improves the efficiency of MRT contrast agent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. A. Abakumov, N. V. Nukolova, M. Sokolsky-Papkov, S. A. Shein, T. O. Sandalova, H. Vishwasrao, N. F. Grinenko, I. L. Gubsky, A. M. Abakumov, A. V. Kabanov, and V. P. Chekhonin, VEGF-targeted magnetic nanoparticles for MRI visualization of brain tumor. Nanomedicine, 11, No. 4, 825-833 (2015).
M. A. Abakumov, S. A. Shein, H. Vishvasrao, N. V. Nukolova, M. Sokol’ski-Papkov, T. O. Sandalova, I. L. Gubskii, N. F. Grinenko, A. V. Kabanov, and V. P. Chekhonin, Visualization of experimental glioma C6 by MRI with magnetic nanoparticles conjugated with monoclonal antibodies to vascular endothelial growth factor. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 154, No. 2, 274-277 (2012).
A. Albanese, P. S. Tang, and C. W. Chan, The effect of nanoparticle size, shape, and surface chemistry on biological systems. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng., 14, 1-16 (2012).
R. Bachmann, R. Conrad, B. Kreft, O. Luzar, W. Block, S. Flacke, D. Pauleit, F. Traber, J. Gieseke, K. Saebo, and H. Schild, Evaluation of a new ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide contrast agent Clariscan, (NC100150) for MRI of renal perfusion: experimental study in an animal model. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging, 16, No. 2, 190-195 (2002).
V. P. Chekhonin, V. P. Baklaushev, G. M. Yusubalieva, A. E. Belorusova, M. V. Gulyaev, E. B. Tsitrin, N. F. Grinenko, O. I. Gurina, and Y. A. Pirogov, Targeted delivery of liposomal nanocontainers to the peritumoral zone of glioma by means of monoclonal antibodies against GFAP and the extracellular loop of Cx43. Nanomedicine, 8, No. 1, 63-70 (2012).
Z. Karimi, L. Karimi, and H. Shokrollahi, Nano-magnetic particles used in biomedicine: core and coating materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl., 33, No. 5, 2465-2475 (2013).
M. M. Lin, K. Kim do, A. J. El Haj, and J. Dobson, Development of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONS) for translation to clinical applications. IEEE Trans. Nanobioscience, 7, No. 4, 298-305 (2008).
K. Lind, M. Kresse, N. P. Debus, and R. H. Muller, A novel formulation for superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) particles enhancing MR lymphography: comparison of physicochemical properties and the in vivo behaviour. J. Drug. Target, 10, No. 3, 221-230 (2002).
M. Longmire, P. L. Choyke, and H. Kobayashi, Clearance properties of nano-sized particles and molecules as imaging agents: considerations and caveats. Nanomedicine (Lond.), 3, No. 5, 703-717 (2008).
K. Ohno, C. Mori, T. Akashi, S. Yoshida, Y. Tago, Y. Tsujii, and Y. Tabata, Fabrication of contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging from polymer-brush-afforded iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles prepared by surface-initiated living radical polymerization. Biomacromolecules, 14, No. 10, 3453-3462 (2013).
D. Patel, A. Kell, B. Simard, B. Xiang, H. Y. Lin, and G. Tian, The cell labeling efficacy, cytotoxicity and relaxivity of copper-activated MRI/PET imaging contrast agents. Biomaterials, 32, No. 4, 1167-1176 (2013).
B. W. Tse, G. J. Cowin, C. Soekmadji, L. Jovanovic, R. S. Vasireddy, M. T. Ling, A. Khatri, T. Liu, B. Thierry, and P. J. Russell, PSMA-targeting iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles enhance MRI of preclinical prostate cancer. Nanomedicine (Lond.), 10, No. 3, 375-386 (2015).
Y. X. Wang, S. M. Hussain, and G. P. Krestin, Superparamagnetic iron oxide contrast agents: physicochemical characteristics and applications in MR imaging. Eur. Radiol., 11, No. 11, 2319-2331 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 161, No. 2, pp. 256-260, February, 2016
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Semkina, A.S., Abakumov, M.A., Abakumov, A.M. et al. Relationship between the Size of Magnetic Nanoparticles and Efficiency of MRT Imaging of Cerebral Glioma in Rats. Bull Exp Biol Med 161, 292–295 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3398-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3398-y