Abstract
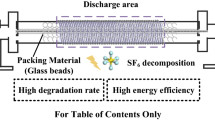
Packed-bed DBD (PB-DBD) plasmas hold promise for effective degradation of greenhouse gases like SF6. In this work, we conducted a combined experimental and theoretical study to investigate the effect of the packing surface structure and the plasma surface discharge on the SF6 degradation in a γ-Al2O3 packing DBD system. Experimental results show that both the hydration effect of the surface (upon moisture) and the presence of excessive reactive gases in the plasma can significantly reduce the SF6 degradation, but they hardly change the discharge behavior. DFT results show that the pre-adsorption of species such as H, OH, H2O and O2 can occupy the active sites (AlIII site) which negatively impacts the SF6 adsorption. H2O molecules pre-adsorbed at neighboring sites can promote the activation of SF6 molecules and lower the reaction barrier for the S-F bond-breaking process. Surface-induced charges and local external electric fields caused by the plasma can both improve the SF6 adsorption and enhance the elongation of the S-F bonds. Our results indicate that both the surface structure of the packing material and the plasma surface discharge are crucial for SF6 degradation performance, and the packing beads should be kept dry during the degradation. This work helps to understand the underlying mechanisms of SF6 degradation in a PB-DBD system.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Christophorou LG, Olthoff JK, Van Brunt RJ (1997) Sulfur hexafluoride and the electric power industry [J]. IEEE Electr Insul Mag 13(5):20–24
Dervos CT, Vassiliou P (2000) Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6): global environmental effects and toxic byproduct formation [J]. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 50(1):137–141
Fang X, Hu X, Janssens-Maenhout G et al (2013) Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) emission estimates for China: an inventory for 1990–2010 and a projection to 2020 [J]. Environ Sci Technol 47(8):3848–3855
Kieffel Y, Irwin T, Ponchon P et al (2016) Green gas to replace SF6 in electrical grids [J]. IEEE Power Energ Mag 14(2):32–39
Reilly J, Prinn R, Harnisch J et al (1999) Multi-gas assessment of the Kyoto protocol [J]. Nature 401(6753):549–555
Zhou S, Teng F, Tong Q (2018) Mitigating Sulfur Hexafluoride (SF6) emission from electrical equipment in China [J]. Sustainability 10(7):2402
Mead I. International energy outlook 2017[J]. US Energy Information Administration, 2017.
Nielsen OK, Plejdrup MS, Winther M, Report DNI et al (2020) Emission Inventories 1990–2018-Submitted under the United Nations framework convention on climate change and the Kyoto protocol [J]. Scientific Report from DCE 2020:900
Tsai CH, Shao JM (2008) Formation of fluorine for abating sulfur hexafluoride in an atmospheric-pressure plasma environment[J]. J Hazard Mater 157(1):201–206
Kashiwagi D, Takai A, Takubo T et al (2009) Catalytic activity of rare earth phosphates for SF6 decomposition and promotion effects of rare earths added into AlPO4[J]. J Colloid Interface Sci 332(1):136–144
Zhang J, Zhou JZ, Liu Q et al (2013) Efficient removal of sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) through reacting with recycled electroplating sludge [J]. Environ Sci Technol 47(12):6493–6499
Holze P, Horn B, Limberg C et al (2014) The activation of sulfur hexafluoride at highly reduced low-coordinate nickel dinitrogen complexes [J]. Angew Chem Int Ed 53(10):2750–2753
Song X, Liu X, Ye Z et al (2009) Photodegradation of SF6 on polyisoprene surface: Implication on elimination of toxic byproducts [J]. J Hazard Mater 168(1):493–500
Govindan M, Gopal RA, Moon IS (2020) Electrochemical sequential reduction and oxidation facilitates the continual ambient temperature degradation of SF6 to nontoxic gaseous compounds [J]. Chem Eng J 382:122881
Zhang X, Xiao H, Tang J et al (2017) Recent advances in decomposition of the most potent greenhouse gas SF6[J]. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 47(18):1763–1782
Lee H, Chang M, Wu K (2004) Abatement of sulfur hexafluoride emissions from the semiconductor manufacturing process by atmospheric-pressure plasmas [J]. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 54(8):960–970
Zhang X, Xiao H, Hu X et al (2018) Effects of reduced electric field on sulfur hexafluoride removal for a double dielectric barrier discharge reactor [J]. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 46(3):563–570
Radoiu M, Hussain S (2009) Microwave plasma removal of sulphur hexafluoride [J]. J Hazard Mater 164(1):39–45
Kim J, Cho C, Shin D et al (2015) Abatement of fluorinated compounds using a 2.45 GHz microwave plasma torch with a reverse vortex plasma reactor [J]. J Hazardous Mater 294:41–46
Shih M, Lee W, Tsai C et al (2002) Decomposition of SF6 in an RF plasma environment [J]. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 52(11):1274–1280
Zhang X, Cui Z, Li Y et al (2018) Abatement of SF6 in the presence of NH3 by dielectric barrier discharge plasma[J]. J Hazard Mater 360:341–348
Cui Z, Zhang X, Yuan T et al (2019) Plasma-assisted abatement of SF6 in a dielectric barrier discharge reactor: investigation of the effect of packing materials[J]. J Phys D Appl Phys 53(2):025205
Cui Z, Zhou C, Jafarzadeh A, et al. (2022) SF6 catalytic degradation in a γ-Al2O3 packed bed plasma system: a combined experimental and theoretical study [J]. High Voltage. 7(6):1048–1058
Bogaerts A, Tu X, Whitehead J et al (2020) The 2020 plasma catalysis roadmap [J]. J Phys D Appl Phys 53(44):443001
Peri JB (1965) Infrared and gravimetric study of the surface hydration of γ-alumina[J]. J Phys Chem 69(1):211–219
Lefevre G, Duc M, Lepeut P et al (2002) Hydration of γ-alumina in water and its effects on surface reactivity[J]. Langmuir 18(20):7530–7537
Fernandez EM, Eglitis RI, Borstel G et al (2007) Ab initio calculations of H2O and O2 adsorption on Al2O3 substrates[J]. Comput Mater Sci 39(3):587–592
Butterworth T, Elder R, Allen R (2016) Effects of particle size on CO2 reduction and discharge characteristics in a packed bed plasma reactor[J]. Chem Eng J 293:55–67
Wang X, Gao Y, Zhang S et al (2019) Nanosecond pulsed plasma assisted dry reforming of CH4: the effect of plasma operating parameters[J]. Appl Energy 243:132–144
Jiang N, Guo L, Qiu C et al (2018) Reactive species distribution characteristics and toluene destruction in the three-electrode DBD reactor energized by different pulsed modes[J]. Chem Eng J 350:12–19
Neyts EC, Ostrikov K, Sunkara MK et al (2015) Plasma catalysis: synergistic effects at the nanoscale[J]. Chem Rev 115(24):13408–13446
Yi Y, Wang X, Jafarzadeh A et al (2021) Plasma-catalytic ammonia reforming of methane over cu-based catalysts for the production of HCN and H2 at reduced temperature[J]. ACS Catal 11(3):1765–1773
Bal KM, Huygh S, Bogaerts A et al (2018) Effect of plasma-induced surface charging on catalytic processes: application to CO2 activation[J]. Plasma Sourc Sci Technol 27(2):024001
Shirazi M, Neyts EC, Bogaerts A (2017) DFT study of Ni-catalyzed plasma dry reforming of methane[J]. Appl Catal B 205:605–614
Hutter J, Iannuzzi M, Schiffmann F et al (2014) cp2k: atomistic simulations of condensed matter systems [J]. Wiley Interdiscipl Rev: Comput Mol Sci 4(1):15–25
VandeVondele J, Krack M, Mohamed F et al (2005) Quickstep: Fast and accurate density functional calculations using a mixed Gaussian and plane waves approach [J]. Comput Phys Commun 167(2):103–128
VandeVondele J, Hutter J (2007) Gaussian basis sets for accurate calculations on molecular systems in gas and condensed phases [J]. J Chem Phys 127(11):114105
Goedecker S, Teter M, Hutter J (1996) Separable dual-space Gaussian pseudopotentials [J]. Phys Rev B 54(3):1703
Perdew J, Burke K, Ernzerhof M (1996) Generalized gradient approximation made simple [J]. Phys Rev Lett 77(18):3865
Grimme S, Antony J, Ehrlich S et al (2010) A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu [J]. J Chem Phys 132(15):154104
Head J, Zerner M (1985) A Broyden—Fletcher—Goldfarb—Shanno optimization procedure for molecular geometries [J]. Chem Phys Lett 122(3):264–270
Henkelman G, Uberuaga BP, Jónsson H (2000) A climbing image nudged elastic band method for finding saddle points and minimum energy paths [J]. J Chem Phys 113(22):9901–9904
Henkelman G, Arnaldsson A, Jónsson H (2006) A fast and robust algorithm for Bader decomposition of charge density [J]. Comput Mater Sci 36(3):354–360
Digne M, Sautet P, Raybaud P et al (2004) Use of DFT to achieve a rational understanding of acid–basic properties of γ-alumina surfaces [J]. J Catal 226(1):54–68
Wischert R, Laurent P, Copéret C et al (2012) γ-Alumina: the essential and unexpected role of water for the structure, stability, and reactivity of “defect” sites [J]. J Am Chem Soc 134(35):14430–14449
Martyna G, Tuckerman M (1999) A reciprocal space based method for treating long range interactions in ab initio and force-field-based calculations in clusters [J]. J Chem Phys 110(6):2810–2821
Jafarzadeh A, Bal K, Bogaerts A et al (2020) Activation of CO2 on copper surfaces: the synergy between electric field, surface morphology, and excess electrons [J]. J Phys Chem C 124(12):6747–6755
Peeters FJJ, Van de Sanden MCM (2014) The influence of partial surface discharging on the electrical characterization of DBDs[J]. Plasma Sourc Sci Technol 24(1):015016
Butterworth T, Allen RWK (2017) Plasma-catalyst interaction studied in a single bead DBD reactor: dielectric constant effect on plasma dynamics[J]. Plasma Sourc Sci Technol 26(6):065008
Wang Q, Zhou X, Dai D et al (2021) Nonlinear feature in the spatial uniformity of an atmospheric helium dielectric barrier discharge with the inter-dielectric gap width enlarged [J]. Plasma Sour Sci Technol 30(5):56
Tsai WT (2007) The decomposition products of sulfur hexafluoride (SF6): reviews of environmental and health risk analysis[J]. J Fluorine Chem 128(11):1345–1352
Zhang X, Cui Z, Li Y et al (2018) Study on degradation of SF6 in the presence of H2O and O2 using dielectric barrier discharge[J]. IEEE Access 6:72748–72756
Zhang X, Yuan T, Cui Zhaolun et al (2020) Plasma-assisted abatement of SF6 in a packed bed plasma reactor: understanding the effect of gas composition[J]. Plasma Sci Technol 22(5):055502
Tian Y, Zhang X, Tang B et al (2019) SF6 abatement in a packed bed plasma reactor: study towards the effect of O2 concentration[J]. RSC Adv 9(60):34827–34836
Xiao H, Zhang X, Hu X et al (2017) Experimental and simulation analysis on by-products of treatment of SF6 using dielectric barrier discharge[J]. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 24(3):1617–1624
Wang W, Kim H, Van Laer K et al (2018) Streamer propagation in a packed bed plasma reactor for plasma catalysis applications [J]. Chem Eng J 334:2467–2479
Deshlahra P, Wolf EE, Schneider WF (2009) A periodic density functional theory analysis of CO chemisorption on Pt (111) in the presence of uniform electric fields[J]. J Phys Chem A 113(16):4125–4133
Zhang QZ, Bogaerts A (2018) Propagation of a plasma streamer in catalyst pores[J]. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 27(3):035009
Cui Z, Meng S, Yi Y et al (2022) Plasma-catalytic methanol synthesis from CO2 hydrogenation over a supported Cu cluster catalyst: insights into the reaction mechanism[J]. ACS Catal 12(2):1326–1337
Acknowledgements
The computational resources and services used in this work were provided by the HPC core facility CalcUA of the Universiteit Antwerpen, and VSC (Flemish Supercomputer Center), funded by the Research Foundation—Flanders (FWO) and the Flemish Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, Z., Zhou, C., Jafarzadeh, A. et al. SF6 Degradation in a γ-Al2O3 Packed DBD System: Effects of Hydration, Reactive Gases and Plasma-Induced Surface Charges. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 43, 635–656 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-023-10320-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-023-10320-3