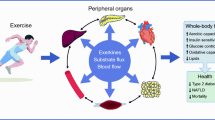
Abstract
Neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and Huntington’s diseases have high prevalence among the elderly. Many strategies have been established to alleviate the symptoms experienced by affected individuals. Recent studies have shown that exercise helps patients with neurological disorders to regain lost physical abilities. PGC1α/FNDC5/BDNF has emerged recently as a critical pathway for neuroprotection. PGC1α is a highly conserved co-activator of transcription factors that preserves and protects neurons against destruction. PGC1α regulates FNDC5 and its processed and secreted peptide Irisin, which has been proposed to play a critical role in energy expenditure and to promote neural differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells. FNDC5 may also increase the expression of the neurotrophic factor BDNF, a neuroprotective agent, in the hippocampus. BDNF is secreted from hippocampus, amygdala, cerebral cortex and hypothalamus neurons and initiates intracellular signaling pathways through TrkB receptors. These pathways have positive feedback on CREB activities and lead to enhancement in PGC1α expression in neurons. Therefore, FNDC5 could behave as a key regulator in neuronal survival and development. This review presents recent findings on the PGC1α/FNDC5/BDNF pathway and its role in neuroprotection, and discusses the controversial promise of irisin as a mediator of the positive benefits of exercise.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 6-OHDA:
-
6-Hydroxy dopamine
- Aβ:
-
Amyloid beta
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- ALS:
-
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- BDNF:
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CREB:
-
cAMP-responsive element binding protein
- DHA:
-
Docosahexaenoicacid
- ERRα:
-
Estrogen-related receptor alpha
- ETC:
-
Electron transport chain
- FA:
-
Friedreich’s ataxia
- FNDC5:
-
Fibronectin type III domain-containing 5
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- HD:
-
Huntington’s disease
- KSS:
-
Kearns–Sayre syndrome
- LTP:
-
Long-term potentiation
- MAO:
-
Monoamine oxidase
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MELSAS:
-
Mitochondrial encephalopathy lactic acidosis and strokes
- mHtt:
-
Mutant huntingtin protein
- Mn-SOD:
-
Manganese superoxide dismutase
- MPTP:
-
1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
- NMDA:
-
N-Methyl-d-aspartate
- NRF:
-
Nuclear respiratory factor
- OXPHOS:
-
Oxidative phosphorylation system
- PARIS:
-
Parkin-interacting substrate
- PBDs:
-
Peroxisome biogenesis disorders
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- PEDs:
-
Peroxisomal enzyme deficiencies
- PEP:
-
Peroxisomal protein
- PGC1α:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ co-activator α
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidyl inositol-3-kinase
- PLCγ:
-
Phospholipase C-γ
- PPARα:
-
Peroxisome proliferator receptor alpha
- PUFAs:
-
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SIRT1:
-
Sirtunin1
- SNP:
-
Single-nucleotide polymorphism
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- TAF4:
-
Transcription initiation factor 4
- TFAM:
-
Mitochondrial transcription factor A
- TR:
-
Thyroid receptor
- TrkB:
-
Tyrosine kinase receptor B
- VDAC:
-
Voltage-dependent anion channels
References
Ahlskog, J. E. (2011). Cheaper, simpler, and better: Tips for treating seniors with Parkinson disease. Mayo Clinic Proceedings, 86, 1211–1216.
Albrecht, E., Norheim, F., Thiede, B., Holen, T., Ohashi, T., Schering, L., et al. (2015). Irisin—A myth rather than an exercise-inducible myokine. Scientific reports, 5, 8889.
Amadoro, G., Corsetti, V., Florenzano, F., Atlante, A., Bobba, A., Nicolin, V., et al. (2014). Morphological and bioenergetic demands underlying the mitophagy in post-mitotic neurons: the pink-parkin pathway. Front Aging Neurosci, 6, 18.
Andreyev, A. Y., Kushnareva, Y. E., Murphy, A. N., & Starkov, A. A. (2015). Mitochondrial ROS metabolism: 10 years later. Biochemistry (Mosc), 80, 517–531.
Antonenkov, V. D., Grunau, S., Ohlmeier, S., & Hiltunen, J. K. (2010). Peroxisomes are oxidative organelles. Antioxidants and Redox Signaling, 13, 525–537.
Ayala, A., Muñoz, M. F., & Argüelles, S. (2014). Lipid peroxidation: Production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2014, 360438.
Aydin, S., Kuloglu, T., Eren, M. N., Celik, A., Yilmaz, M., Kalayci, M., et al. (2014). Cardiac, skeletal muscle and serum irisin responses to with or without water exercise in young and old male rats: Cardiac muscle produces more irisin than skeletal muscle. Peptides, 52, 68–73.
Baes, M., & Aubourg, P. (2009). Peroxisomes, myelination, and axonal integrity in the CNS. Neuroscientist, 15, 367–379.
Baes, M., & Van Veldhoven, P. P. (2006). Generalised and conditional inactivation of Pex genes in mice. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1763, 1785–1793.
Baines, C. P. (2010). Role of the mitochondrion in programmed necrosis. Frontiers in Physiology, 1, 156.
Balaban, R. S., Nemoto, S., & Finkel, T. (2005). Mitochondria, oxidants, and aging. Cell, 120, 483–495.
Bennett, S. A., Valenzuela, N., Xu, H., Franko, B., Fai, S., & Figeys, D. (2013). Using neurolipidomics to identify phospholipid mediators of synaptic (dys)function in Alzheimer’s Disease. Frontiers in Physiology, 4, 168.
Binder, D. K., & Scharfman, H. E. (2004). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Growth Factors, 22, 123–131.
Blesa, J., Trigo-Damas, I., Quiroga-Varela, A., Jackson-Lewis, V.R. (2015). Oxidative stress and Parkinson’s disease. Front Neuroanat, 9, 91.
Boström, P., Wu, J., Jedrychowski, M. P., Korde, A., Ye, L., Lo, J. C., et al. (2012). A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature, 481, 463–468.
Bordt, E.A.,& Polster, B.M. (2014). NADPH oxidase- and mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species in proinflammatory microglial activation: a bipartisan affair? Free Radic Biol Med, 76, 34–46.
Braverman, N. E., & Moser, A. B. (2012). Functions of plasmalogen lipids in health and disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1822, 1442–1452.
Calon, F., Lim, G. P., Yang, F., Morihara, T., Teter, B., Ubeda, O., et al. (2004). Docosahexaenoic acid protects from dendritic pathology in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Neuron, 43, 633–645.
Carlezon, W. A., Duman, R. S., & Nestler, E. J. (2005). The many faces of CREB. Trends in Neurosciences, 28, 436–445.
Castillo-Quan, J. I. (2011). Parkin’ control: Regulation of PGC-1α through PARIS in Parkinson’s disease. Disease Models and Mechanisms, 4, 427–429.
Chapman, P. F., White, G. L., Jones, M. W., Cooper-Blacketer, D., Marshall, V. J., Irizarry, M., et al. (1999). Impaired synaptic plasticity and learning in aged amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice. Nature Neuroscience, 2, 271–276.
Chaturvedi, R. K., & Beal, M. F. (2013). Mitochondrial diseases of the brain. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 63, 1–29.
Chen, H., McCaffery, J. M., & Chan, D. C. (2007). Mitochondrial fusion protects against neurodegeneration in the cerebellum. Cell, 130, 548–562.
Chen, Z. Y., Patel, P. D., Sant, G., Meng, C. X., Teng, K. K., Hempstead, B. L., & Lee, F. S. (2004). Variant brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) (Met66) alters the intracellular trafficking and activity-dependent secretion of wild-type BDNF in neurosecretory cells and cortical neurons. Journal of Neuroscience, 24, 4401–4411.
Ciccone, S., Maiani, E., Bellusci, G., Diederich, M., & Gonfloni, S. (2013). Parkinson’s disease: A complex interplay of mitochondrial DNA alterations and oxidative stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14, 2388–2409.
Clark, J., Reddy, S., Zheng, K., Betensky, R. A., & Simon, D. K. (2011). Association of PGC-1alpha polymorphisms with age of onset and risk of Parkinson’s disease. BMC Medical Genetics, 12, 69.
Connolly, A. M., Chez, M., Streif, E. M., Keeling, R. M., Golumbek, P. T., Kwon, J. M., et al. (2006). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and autoantibodies to neural antigens in sera of children with autistic spectrum disorders, Landau–Kleffner syndrome, and epilepsy. Biological Psychiatry, 59, 354–363.
Conquer, J. A., Tierney, M. C., Zecevic, J., Bettger, W. J., & Fisher, R. H. (2000). Fatty acid analysis of blood plasma of patients with Alzheimer’s disease, other types of dementia, and cognitive impairment. Lipids, 35, 1305–1312.
Corona, J. C., & Duchen, M. R. (2015). PPARγ and PGC-1α as therapeutic targets in Parkinson’s. Neurochemical Research, 40, 308–316.
Cotman, C. W., Berchtold, N. C., & Christie, L. A. (2007). Exercise builds brain health: Key roles of growth factor cascades and inflammation. Trends in Neurosciences, 30, 464–472.
Cui, L., Jeong, H., Borovecki, F., Parkhurst, C. N., Tanese, N., & Krainc, D. (2006). Transcriptional repression of PGC-1alpha by mutant huntingtin leads to mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegeneration. Cell, 127, 59–69.
del Río, L. A., Corpas, F. J., Sandalio, L. M., Palma, J. M., Gómez, M., & Barroso, J. B. (2002). Reactive oxygen species, antioxidant systems and nitric oxide in peroxisomes. Journal of Experimental Botany, 53, 1255–1272.
Desai, N. S., Rutherford, L. C., & Turrigiano, G. G. (1999). BDNF regulates the intrinsic excitability of cortical neurons. Learning and Memory, 6, 284–291.
Dun, S. L., Lyu, R. M., Chen, Y. H., Chang, J. K., Luo, J. J., & Dun, N. J. (2013). Irisin-immunoreactivity in neural and non-neural cells of the rodent. Neuroscience, 240, 155–162.
Dwivedi, Y. (2009). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: Role in depression and suicide. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment, 5, 433–449.
Edmondson, D. E. (2014). Hydrogen peroxide produced by mitochondrial monoamine oxidase catalysis: biological implications. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 20, 155–160.
Eichner, L. J., & Giguère, V. (2011). Estrogen related receptors (ERRs): A new dawn in transcriptional control of mitochondrial gene networks. Mitochondrion, 11, 544–552.
Erickson, H. P. (2013). Irisin and FNDC5 in retrospect: An exercise hormone or a transmembrane receptor? Adipocyte, 2, 289–293.
Evans, R. M. (2005). The nuclear receptor superfamily: A rosetta stone for physiology. Molecular Endocrinology, 19, 1429–1438.
Exner, N., Lutz, A.K., Haass, C., Winklhofer, K.F. (2012). Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease: molecular mechanisms and pathophysiological consequences. EMBO J, 31(14), 3038–3062.
Farrar, G. J., Chadderton, N., Kenna, P. F., & Millington-Ward, S. (2013). Mitochondrial disorders: Aetiologies, models systems, and candidate therapies. Trends in Genetics, 29, 488–497.
Ferreiro, E., Baldeiras, I., Ferreira, I. L., Costa, R. O., Rego, A. C., Pereira, C. F., & Oliveira, C. R. (2012). Mitochondrial- and endoplasmic reticulum-associated oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease: From pathogenesis to biomarkers. International Journal of Cell Biology, 2012, 735206.
Ferrer-Martínez, A., Ruiz-Lozano, P., & Chien, K. R. (2002). Mouse PeP: A novel peroxisomal protein linked to myoblast differentiation and development. Developmental Dynamics, 224, 154–167.
Fiore, M., Chaldakov, G. N., & Aloe, L. (2009). Nerve growth factor as a signaling molecule for nerve cells and also for the neuroendocrine-immune systems. Reviews in the Neurosciences, 20, 133–145.
Forouzanfar, M., Rabiee, F., Ghaedi, K., Beheshti, S., Tanhaei, S., Shoaraye Nejati, A., et al. (2015). Fndc5 overexpression facilitated neural differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells. Cell Biology International, 39, 629–637.
Fransen, M., Nordgren, M., Wang, B., & Apanasets, O. (2012). Role of peroxisomes in ROS/RNS-metabolism: Implications for human disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1822, 1363–1373.
Fujiwara, H., Hasegawa, M., Dohmae, N., Kawashima, A., Masliah, E., Goldberg, M. S., et al. (2002). alpha-Synuclein is phosphorylated in synucleinopathy lesions. Nature Cell Biology, 4, 160–164.
Ghahrizjani, F. A., Ghaedi, K., Salamian, A., Tanhaei, S., Nejati, A. S., Salehi, H., et al. (2015). Enhanced expression of FNDC5 in human embryonic stem cell-derived neural cells along with relevant embryonic neural tissues. Gene, 557, 123–129.
Giampà, C., Montagna, E., Dato, C., Melone, M. A., Bernardi, G., & Fusco, F. R. (2013). Systemic delivery of recombinant brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the R6/2 mouse model of Huntington’s disease. PLoS One, 8, e64037.
Ginsberg, L., Rafique, S., Xuereb, J. H., Rapoport, S. I., & Gershfeld, N. L. (1995). Disease and anatomic specificity of ethanolamine plasmalogen deficiency in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Brain Research, 698, 223–226.
Goncalves, R. L., Rothschild, D. E., Quinlan, C. L., Scott, G. K., Benz, C. C., & Brand, M. D. (2014). Sources of superoxide/H2O2 during mitochondrial proline oxidation. Redox Biology, 2, 901–909.
Green, D. R., & Kroemer, G. (2004). The pathophysiology of mitochondrial cell death. Science, 305, 626–629.
Greenberg, M. E., Xu, B., Lu, B., & Hempstead, B. L. (2009). New insights in the biology of BDNF synthesis and release: implications in CNS function. Journal of Neuroscience, 29, 12764–12767.
Guo, C., Sun, L., Chen, X., & Zhang, D. (2013). Oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage and neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regeneration Research, 8, 2003–2014.
Haas, R. H., Parikh, S., Falk, M. J., Saneto, R. P., Wolf, N. I., Darin, N., et al. (2008). The in-depth evaluation of suspected mitochondrial disease. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism, 94, 16–37.
Han, J.Y., Kim, J.S., Son, J.H. (2014). Mitochondrial homeostasis molecules: regulation by a trio of recessive Parkinson's disease genes. Exp Neurobiol, 23(4), 345–351.
Handschin, C. (2009). The biology of PGC-1α and its therapeutic potential. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 30, 322–329.
Hashemi, M. S., Ghaedi, K., Salamian, A., Karbalaie, K., Emadi-Baygi, M., Tanhaei, S., et al. (2013). Fndc5 knockdown significantly decreased neural differentiation rate of mouse embryonic stem cells. Neuroscience, 231, 296–304.
Herben-Dekker, M., van Oostrom, J. C., Roos, R. A., Jurgens, C. K., Witjes-Ané, M. N., Kremer, H. P., et al. (2014). Striatal metabolism and psychomotor speed as predictors of motor onset in Huntington’s disease. Journal of Neurology, 261, 1387–1397.
Huang, E. J., & Reichardt, L. F. (2001). Neurotrophins: Roles in neuronal development and function. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 24, 677–736.
Hwang, O. (2013). Role of oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurobiol, 22(1), 11–17.
Ivanov, I.P., Firth, A.E., Michel, A.M., Atkins, J.F., Baranov, P.V. (2011). Identification of evolutionarily conserved non-AUG-initiated N-terminal extensions in human coding sequences. Nucleic Acids Res, 39(10), 4220–4234.
Ivashchenko, O., Van Veldhoven, P. P., Brees, C., Ho, Y. S., Terlecky, S. R., & Fransen, M. (2011). Intraperoxisomal redox balance in mammalian cells: Oxidative stress and interorganellar cross-talk. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 22, 1440–1451.
Jin, Y. N., & Johnson, G. V. (2010). The interrelationship between mitochondrial dysfunction and transcriptional dysregulation in Huntington disease. Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes, 42, 199–205.
Johnson, W. T., Johnson, L. A., & Lukaski, H. C. (2005). Serum superoxide dismutase 3 (extracellular superoxide dismutase) activity is a sensitive indicator of Cu status in rats. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 16, 682–692.
Johri, A., & Beal, M. F. (2012). Mitochondrial dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 342, 619–630.
Kalmijn, S., Launer, L. J., Ott, A., Witteman, J. C., Hofman, A., & Breteler, M. M. (1997). Dietary fat intake and the risk of incident dementia in the Rotterdam Study. Annals of Neurology, 42, 776–782.
Kassmann, C. M., Lappe-Siefke, C., Baes, M., Brügger, B., Mildner, A., Werner, H. B., et al. (2007). Axonal loss and neuroinflammation caused by peroxisome-deficient oligodendrocytes. Nature Genetics, 39, 969–976.
Katsouri, L., Parr, C., Bogdanovic, N., Willem, M., & Sastre, M. (2011). PPARγ co-activator-1α (PGC-1α) reduces amyloid-β generation through a PPARγ-dependent mechanism. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 25, 151–162.
Kelly, D. P., & Scarpulla, R. C. (2004). Transcriptional regulatory circuits controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and function. Genes and Development, 18, 357–368.
Keogh, M.J., Chinnery, P.F. (2015). Mitochondrial DNA mutations in neurodegeneration. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1847(11), 1401–1411.
Kobilo, T., Liu, Q. R., Gandhi, K., Mughal, M., Shaham, Y., & van Praag, H. (2011). Running is the neurogenic and neurotrophic stimulus in environmental enrichment. Learning and Memory, 18, 605–609.
Koepke, J. I., Nakrieko, K. A., Wood, C. S., Boucher, K. K., Terlecky, L. J., Walton, P. A., & Terlecky, S. R. (2007). Restoration of peroxisomal catalase import in a model of human cellular aging. Traffic, 8, 1590–1600.
Kotiadis, V. N., Duchen, M. R., & Osellame, L. D. (2014). Mitochondrial quality control and communications with the nucleus are important in maintaining mitochondrial function and cell health. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1840, 1254–1265.
Kou, J., Kovacs, G. G., Höftberger, R., Kulik, W., Brodde, A., Forss-Petter, S., et al. (2011). Peroxisomal alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathologica, 122, 271–283.
Kressler, D., Schreiber, S. N., Knutti, D., & Kralli, A. (2002). The PGC-1-related protein PERC is a selective coactivator of estrogen receptor alpha. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277, 13918–13925.
Lee, P., Linderman, J. D., Smith, S., Brychta, R. J., Wang, J., Idelson, C., et al. (2014). Irisin and FGF21 are cold-induced endocrine activators of brown fat function in humans. Cell Metabolism, 19, 302–309.
Legros, F., Malka, F., Frachon, P., Lombès, A., & Rojo, M. (2004). Organization and dynamics of human mitochondrial DNA. Journal of Cell Science, 117, 2653–2662.
Lezi, E., & Swerdlow, R. H. (2012). Mitochondria in neurodegeneration. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 942, 269–286.
Lin, M. T., & Beal, M. F. (2006). Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature, 443, 787–795.
Lin, J., Puigserver, P., Donovan, J., Tarr, P., & Spiegelman, B. M. (2002a). Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1beta (PGC-1beta), a novel PGC-1-related transcription coactivator associated with host cell factor. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277, 1645–1648.
Lin, M.Y., & Sheng, Z.H. (2015). Regulation of mitochondrial transport in neurons. Exp Cell Res, 334(1), 35–44.
Lin, J., Wu, P. H., Tarr, P. T., Lindenberg, K. S., St-Pierre, J., Zhang, C. Y., et al. (2004). Defects in adaptive energy metabolism with CNS-linked hyperactivity in PGC-1alpha null mice. Cell, 119, 121–135.
Lin, J., Wu, H., Tarr, P. T., Zhang, C. Y., Wu, Z., Boss, O., et al. (2002b). Transcriptional co-activator PGC-1 alpha drives the formation of slow-twitch muscle fibres. Nature, 418, 797–801.
Lodhi, I. J., & Semenkovich, C. F. (2014). Peroxisomes: A nexus for lipid metabolism and cellular signaling. Cell Metabolism, 19, 380–392.
Lopez-Huertas, E., Charlton, W. L., Johnson, B., Graham, I. A., & Baker, A. (2000). Stress induces peroxisome biogenesis genes. EMBO Journal, 19, 6770–6777.
Mailloux, R. J. (2015). Teaching the fundamentals of electron transfer reactions in mitochondria and the production and detection of reactive oxygen species. Redox Biology, 4, 381–398.
Martin, E., Betuing, S., Pagès, C., Cambon, K., Auregan, G., Deglon, N., et al. (2011). Mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase 1-induced neuroprotection in Huntington’s disease: role on chromatin remodeling at the PGC-1-alpha promoter. Human Molecular Genetics, 20, 2422–2434.
Mattson, M. P. (2012). Energy intake and exercise as determinants of brain health and vulnerability to injury and disease. Cell Metabolism, 16, 706–722.
McAllister, A. K. (2001). Neurotrophins and neuronal differentiation in the central nervous system. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 58, 1054–1060.
McGill, J. K., & Beal, M. F. (2006). PGC-1alpha, a new therapeutic target in Huntington’s disease? Cell, 127, 465–468.
Milnerwood, A. J., & Raymond, L. A. (2010). Early synaptic pathophysiology in neurodegeneration: Insights from Huntington’s disease. Trends in Neurosciences, 33, 513–523.
Mochel, F., & Haller, R. G. (2011). Energy deficit in Huntington disease: Why it matters. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 121, 493–499.
Momose, Y., Murata, M., Kobayashi, K., Tachikawa, M., Nakabayashi, Y., Kanazawa, I., & Toda, T. (2002). Association studies of multiple candidate genes for Parkinson’s disease using single nucleotide polymorphisms. Annals of Neurology, 51, 133–136.
Monteiro-Junior, R. S., Cevada, T., Oliveira, B. R., Lattari, E., Portugal, E. M., Carvalho, A., & Deslandes, A. C. (2015). We need to move more: Neurobiological hypotheses of physical exercise as a treatment for Parkinson’s disease. Medical Hypotheses,. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2015.07.011
Moon, H. S., Dincer, F., & Mantzoros, C. S. (2013). Pharmacological concentrations of irisin increase cell proliferation without influencing markers of neurite outgrowth and synaptogenesis in mouse H19-7 hippocampal cell lines. Metabolism, 62, 1131–1136.
Moreira, P. I., Santos, M. S., Seiça, R., & Oliveira, C. R. (2007). Brain mitochondrial dysfunction as a link between Alzheimer’s disease and diabetes. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 257, 206–214.
Mudò, G., Mäkelä, J., Di Liberto, V., Tselykh, T. V., Olivieri, M., Piepponen, P., et al. (2012). Transgenic expression and activation of PGC-1α protect dopaminergic neurons in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 69, 1153–1165.
Murphy, M. P. (2009). How mitochondria produce reactive oxygen species. Biochemical Journal, 417, 1–13.
Nagley, P., Higgins, G. C., Atkin, J. D., & Beart, P. M. (2010). Multifaceted deaths orchestrated by mitochondria in neurones. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1802, 167–185.
Nicholls, D. G. (2008). Oxidative stress and energy crises in neuronal dysfunction. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1147, 53–60.
Nixon, R. A., Cataldo, A. M., & Mathews, P. M. (2000). The endosomal–lysosomal system of neurons in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis: A review. Neurochemical Research, 25, 1161–1172.
Obulesu, M., & Lakshmi, M. J. (2014). Apoptosis in Alzheimer’s disease: an understanding of the physiology, pathology and therapeutic avenues. Neurochemical Research, 39, 2301–2312.
Ostadsharif, M., Ghaedi, K., Hossein Nasr-Esfahani, M., Mojbafan, M., Tanhaie, S., Karbalaie, K., & Baharvand, H. (2011). The expression of peroxisomal protein transcripts increased by retinoic acid during neural differentiation. Differentiation, 81, 127–132.
Outeiro, T. F., Marques, O., & Kazantsev, A. (2008). Therapeutic role of sirtuins in neurodegenerative disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1782, 363–369.
Payne, B. A., & Chinnery, P. F. (2015). Mitochondrial dysfunction in aging: Much progress but many unresolved questions. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1847(11), 1347–1353.
Petzold, A., Psotta, L., Brigadski, T., Endres, T., & Lessmann, V. (2015). Chronic BDNF deficiency leads to an age-dependent impairment in spatial learning. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 120, 52–60.
Phillips, C., Baktir, M. A., Srivatsan, M., & Salehi, A. (2014). Neuroprotective effects of physical activity on the brain: a closer look at trophic factor signaling. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 8, 170.
Picconi, B., Piccoli, G., & Calabresi, P. (2012). Synaptic dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 970, 553–572.
Picone, P., Nuzzo, D., Caruana, L., Scafidi, V., Di Carlo, M. (2014). Mitochondrial dysfunction: different routes to Alzheimer's disease therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2014, 780179.
Pizzorusso, T., Ratto, G. M., Putignano, E., & Maffei, L. (2000). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor causes cAMP response element-binding protein phosphorylation in absence of calcium increases in slices and cultured neurons from rat visual cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, 20, 2809–2816.
Przedborski, S., Vila, M., & Jackson-Lewis, V. (2003). Neurodegeneration: What is it and where are we? Journal of Clinical Investigation, 111, 3–10.
Puigserver, P., Wu, Z., Park, C. W., Graves, R., Wright, M., & Spiegelman, B. M. (1998). A cold-inducible coactivator of nuclear receptors linked to adaptive thermogenesis. Cell, 92, 829–839.
Qin, W., Haroutunian, V., Katsel, P., Cardozo, C. P., Ho, L., Buxbaum, J. D., & Pasinetti, G. M. (2009). PGC-1alpha expression decreases in the Alzheimer disease brain as a function of dementia. Archives of Neurology, 66, 352–361.
Qin, W., Yang, T., Ho, L., Zhao, Z., Wang, J., Chen, L., et al. (2006). Neuronal SIRT1 activation as a novel mechanism underlying the prevention of Alzheimer disease amyloid neuropathology by calorie restriction. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281, 21745–21754.
Rabiee, F., Forouzanfar, M., Ghazvini Zadegan, F., Tanhaei, S., Ghaedi, K., Motovali Bashi, M., et al. (2014). Induced expression of Fndc5 significantly increased cardiomyocyte differentiation rate of mouse embryonic stem cells. Gene, 551, 127–137.
Radak, Z., Chung, H. Y., & Goto, S. (2005). Exercise and hormesis: Oxidative stress-related adaptation for successful aging. Biogerontology, 6, 71–75.
Raschke, S., Elsen, M., Gassenhuber, H., Sommerfeld, M., Schwahn, U., Brockmann, B., et al. (2013). Evidence against a beneficial effect of irisin in humans. PLoS ONE, 8, e73680.
Reddy, P. H. (2009). Role of mitochondria in neurodegenerative diseases: Mitochondria as a therapeutic target in Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Spectrums, 14, 8–13. discussion 16–18.
Reichardt, L. F. (2006). Neurotrophin-regulated signalling pathways. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological sciences, 361, 1545–1564.
Rinnerthaler, M., Bischof, J., Streubel, M. K., Trost, A., & Richter, K. (2015). Oxidative stress in aging human skin. Biomolecules, 5, 545–589.
Rossignol, D. A., & Frye, R. E. (2012). A review of research trends in physiological abnormalities in autism spectrum disorders: immune dysregulation, inflammation, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and environmental toxicant exposures. Molecular Psychiatry, 17, 389–401.
Ruetenik, A., & Barrientos, A. (2015) Dietary restriction, mitochondrial function and aging: From yeast to humans. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1847(11), 1434–1447.
Santos, M. J., Quintanilla, R. A., Toro, A., Grandy, R., Dinamarca, M. C., Godoy, J. A., & Inestrosa, N. C. (2005). Peroxisomal proliferation protects from beta-amyloid neurodegeneration. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 41057–41068.
Scarpulla, R. C. (2008). Transcriptional paradigms in mammalian mitochondrial biogenesis and function. Physiological Reviews, 88, 611–638.
Schäbitz, W. R., Sommer, C., Zoder, W., Kiessling, M., Schwaninger, M., & Schwab, S. (2000). Intravenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor reduces infarct size and counterregulates Bax and Bcl-2 expression after temporary focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke, 31, 2212–2217.
Schon, E. A., DiMauro, S., Hirano, M., & Gilkerson, R. W. (2010). Therapeutic prospects for mitochondrial disease. Trends in Molecular Medicine, 16, 268–276.
Schreiber, S. N., Emter, R., Hock, M. B., Knutti, D., Cardenas, J., Podvinec, M., et al. (2004). The estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRalpha) functions in PPARgamma coactivator 1alpha (PGC-1alpha)-induced mitochondrial biogenesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 101, 6472–6477.
Selkoe, D. J., & Schenk, D. (2003). Alzheimer’s disease: Molecular understanding predicts amyloid-based therapeutics. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology, 43, 545–584.
Sen, S., Nesse, R. M., Stoltenberg, S. F., Li, S., Gleiberman, L., Chakravarti, A., et al. (2003). A BDNF coding variant is associated with the NEO personality inventory domain neuroticism, a risk factor for depression. Neuropsychopharmacology, 28, 397–401.
Sharon, R., Bar-Joseph, I., Frosch, M. P., Walsh, D. M., Hamilton, J. A., & Selkoe, D. J. (2003a). The formation of highly soluble oligomers of alpha-synuclein is regulated by fatty acids and enhanced in Parkinson’s disease. Neuron, 37, 583–595.
Sharon, R., Bar-Joseph, I., Mirick, G. E., Serhan, C. N., & Selkoe, D. J. (2003b). Altered fatty acid composition of dopaminergic neurons expressing alpha-synuclein and human brains with alpha-synucleinopathies. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 49874–49881.
Sheikh, F. G., Pahan, K., Khan, M., Barbosa, E., & Singh, I. (1998). Abnormality in catalase import into peroxisomes leads to severe neurological disorder. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 95, 2961–2966.
Sheng, B., Wang, X., Su, B., Lee, H. G., Casadesus, G., Perry, G., & Zhu, X. (2012). Impaired mitochondrial biogenesis contributes to mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neurochemistry, 120, 419–429.
Shin, J. H., Ko, H. S., Kang, H., Lee, Y., Lee, Y. I., Pletinkova, O., et al. (2011). PARIS (ZNF746) repression of PGC-1α contributes to neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Cell, 144, 689–702.
Shutt, T.E.,& McBride, H.M. (2013). Staying cool in difficult times: mitochondrial dynamics, quality control and the stress response. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1833(2), 417–424.
Song, W., Chen, J., Petrilli, A., Liot, G., Klinglmayr, E., Zhou, Y., et al. (2011). Mutant huntingtin binds the mitochondrial fission GTPase dynamin-related protein-1 and increases its enzymatic activity. Nature Medicine, 17, 377–382.
Spiegelman, B. M. (2013). Banting Lecture 2012 Regulation of adipogenesis: Toward new therapeutics for metabolic disease. Diabetes, 62, 1774–1782.
Steinberg, S. J., Dodt, G., Raymond, G. V., Braverman, N. E., Moser, A. B., & Moser, H. W. (2006). Peroxisome biogenesis disorders. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1763, 1733–1748.
St-Pierre, J., Drori, S., Uldry, M., Silvaggi, J. M., Rhee, J., Jäger, S., et al. (2006). Suppression of reactive oxygen species and neurodegeneration by the PGC-1 transcriptional coactivators. Cell, 127, 397–408.
Sun, M., Kong, L., Wang, X., Lu, X. G., Gao, Q., & Geller, A. I. (2005). Comparison of the capability of GDNF, BDNF, or both, to protect nigrostriatal neurons in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Research, 1052, 119–129.
Tapia-Arancibia, L., Aliaga, E., Silhol, M., & Arancibia, S. (2008). New insights into brain BDNF function in normal aging and Alzheimer disease. Brain Research Reviews, 59, 201–220.
Tapia-Arancibia, L., Rage, F., Givalois, L., & Arancibia, S. (2004). Physiology of BDNF: Focus on hypothalamic function. Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology, 25, 77–107.
Tillement, L., Lecanu, L., & Papadopoulos, V. (2011). Alzheimer’s disease: Effects of β-amyloid on mitochondria. Mitochondrion, 11, 13–21.
Tong, L., Balazs, R., Thornton, P. L., & Cotman, C. W. (2004). Beta-amyloid peptide at sublethal concentrations downregulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor functions in cultured cortical neurons. Journal of Neuroscience, 24, 6799–6809.
Trempe, J.F., & Fon, E.A. (2013). Structure and Function of Parkin, PINK1, and DJ-1, the Three Musketeers of Neuroprotection. Front Neurol, 4, 38.
Tretter, L., Sipos, I., & Adam-Vizi, V. (2004). Initiation of neuronal damage by complex I deficiency and oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Neurochemical Research, 29, 569–577.
Tsai, S. J. (2006). TrkB partial agonists: potential treatment strategy for epilepsy, mania, and autism. Medical Hypotheses, 66, 173–175.
Tsunemi, T., Ashe, T. D., Morrison, B. E., Soriano, K. R., Au, J., Roque, R. A., et al. (2012). PGC-1α rescues Huntington’s disease proteotoxicity by preventing oxidative stress and promoting TFEB function. Science Translational Medicine, 4, 142ra197.
van der Valk, P., Gille, J. J., Oostra, A. B., Roubos, E. W., Sminia, T., & Joenje, H. (1985). Characterization of an oxygen-tolerant cell line derived from Chinese hamster ovary. Antioxygenic enzyme levels and ultrastructural morphometry of peroxisomes and mitochondria. Cell and Tissue Research, 239, 61–68.
Vega, R. B., Huss, J. M., & Kelly, D. P. (2000). The coactivator PGC-1 cooperates with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha in transcriptional control of nuclear genes encoding mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation enzymes. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 20, 1868–1876.
Ventriglia, M., Bocchio Chiavetto, L., Benussi, L., Binetti, G., Zanetti, O., Riva, M. A., & Gennarelli, M. (2002). Association between the BDNF 196 A/G polymorphism and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Molecular Psychiatry, 7, 136–137.
Vila, M., & Przedborski, S. (2003). Targeting programmed cell death in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 4, 365–375.
Villena, J. A. (2015). New insights into PGC-1 coactivators: redefining their role in the regulation of mitochondrial function and beyond. FEBS Journal, 282, 647–672.
Volakakis, N., Kadkhodaei, B., Joodmardi, E., Wallis, K., Panman, L., Silvaggi, J., et al. (2010). NR4A orphan nuclear receptors as mediators of CREB-dependent neuroprotection. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 107, 12317–12322.
Wallace, D. C., & Fan, W. (2009). The pathophysiology of mitochondrial disease as modeled in the mouse. Genes and Development, 23, 1714–1736.
Wanders, R. J., & Waterham, H. R. (2005). Peroxisomal disorders I: Biochemistry and genetics of peroxisome biogenesis disorders. Clinical Genetics, 67, 107–133.
Wanders, R. J., & Waterham, H. R. (2006). Peroxisomal disorders: The single peroxisomal enzyme deficiencies. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1763, 1707–1720.
Wang, R., Li, J. J., Diao, S., Kwak, Y. D., Liu, L., Zhi, L., et al. (2013). Metabolic stress modulates Alzheimer’s β-secretase gene transcription via SIRT1-PPARγ-PGC-1 in neurons. Cell Metabolism, 17, 685–694.
Wenz, T. (2009). PGC-1alpha activation as a therapeutic approach in mitochondrial disease. IUBMB Life, 61, 1051–1062.
Wenz, T. (2011). Mitochondria and PGC-1α in aging and age-associated diseases. Journal of Aging Research, 2011, 810619.
West, A. P., Shadel, G. S., & Ghosh, S. (2011). Mitochondria in innate immune responses. Nature Reviews Immunology, 11, 389–402.
Weydt, P., Soyal, S. M., Gellera, C., Didonato, S., Weidinger, C., Oberkofler, H., et al. (2009). The gene coding for PGC-1alpha modifies age at onset in Huntington’s Disease. Molecular neurodegeneration, 4, 3.
Winterbourn, C. C. (1995). Toxicity of iron and hydrogen peroxide: The Fenton reaction. Toxicology Letters, 82–83, 969–974.
Witte, M. E., Geurts, J. J., de Vries, H. E., van der Valk, P., & van Horssen, J. (2010). Mitochondrial dysfunction: A potential link between neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration? Mitochondrion, 10, 411–418.
Wood, C. S., Koepke, J. I., Teng, H., Boucher, K. K., Katz, S., Chang, P., et al. (2006). Hypocatalasemic fibroblasts accumulate hydrogen peroxide and display age-associated pathologies. Traffic, 7, 97–107.
Wrann, C. D., White, J. P., Salogiannnis, J., Laznik-Bogoslavski, D., Wu, J., Ma, D., et al. (2013). Exercise induces hippocampal BDNF through a PGC-1α/FNDC5 pathway. Cell Metabolism, 18, 649–659.
Wu, Z., Huang, X., Feng, Y., Handschin, C., Gullicksen, P. S., Bare, O., et al. (2006). Transducer of regulated CREB-binding proteins (TORCs) induce PGC-1alpha transcription and mitochondrial biogenesis in muscle cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 103, 14379–14384.
Wu, Z., Puigserver, P., Andersson, U., Zhang, C., Adelmant, G., Mootha, V., et al. (1999). Mechanisms controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and respiration through the thermogenic coactivator PGC-1. Cell, 98, 115–124.
Yakunin, E., Moser, A., Loeb, V., Saada, A., Faust, P., Crane, D. I., et al. (2010). alpha-Synuclein abnormalities in mouse models of peroxisome biogenesis disorders. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 88, 866–876.
Yang, L., Long, Q., Liu, J., Tang, H., Li, Y., Bao, F., Qin, D., Pei, D., Liu, X. (2015). Mitochondrial fusion provides an ‘initial metabolic complementation’ controlled by mtDNA. Cell Mol Life Sci, 72(13):2585-2598.
Yu, S. P. (2003). Na(+), K(+)-ATPase: the new face of an old player in pathogenesis and apoptotic/hybrid cell death. Biochemical Pharmacology, 66, 1601–1609.
Zhang, Y., Ma, K., Song, S., Elam, M. B., Cook, G. A., & Park, E. A. (2004). Peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1 alpha (PGC-1 alpha) enhances the thyroid hormone induction of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I (CPT-I alpha). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 53963–53971.
Zhao, W., Varghese, M., Yemul, S., Pan, Y., Cheng, A., Marano, P., et al. (2011). Peroxisome proliferator activator receptor gamma coactivator-1alpha (PGC-1α) improves motor performance and survival in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Molecular Neurodegeneration, 6, 51.
Zheng, B., Liao, Z., Locascio, J. J., Lesniak, K. A., Roderick, S. S., Watt, M. L., et al. (2010). PGC-1α, a potential therapeutic target for early intervention in Parkinson’s disease. Science Translational Medicine, 2, 52ra73.
Zorzano, A., & Claret, M. (2015). Implications of mitochondrial dynamics on neurodegeneration and on hypothalamic dysfunction. Front Aging Neurosci, 7, 101.
Acknowledgments
We thank all of our colleagues at the Royan Institute for Biotechnology who contributed to the work discussed in this review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jodeiri Farshbaf, M., Ghaedi, K., Megraw, T.L. et al. Does PGC1α/FNDC5/BDNF Elicit the Beneficial Effects of Exercise on Neurodegenerative Disorders?. Neuromol Med 18, 1–15 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-015-8370-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-015-8370-x