Abstract
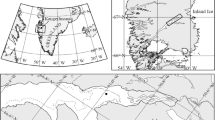
Horizontal variation of first-year landfast sea ice properties was studied in the Gulf of Finland, the Baltic Sea. Several scales of variation were considered; a number of arrays with core spacings of 0.2, 2 and 20 m were sampled at different stages of the ice season for small-scale patchiness. Spacing between these arrays was from hundreds of meters to kilometers to study mesoscale variability, and once an onshore–offshore 40-km transect was sampled to study regional scale variability. Measured variables included salinity, stable oxygen isotopes (δ18O), chlorophyll a (chl-a), nutrients and dissolved organic carbon. On a large scale, a combination of variations in the under-ice water salinity (ice porosity), nutrient supply and the stage of ice development control the build-up of ice algal biomass. At scales of hundreds of meters to kilometers, there was significant variability in several parameters (salinity, chl-a, snow depth and ice thickness). Analyses of the data from the arrays did not show evidence of significant patchiness at scales <20 m for algal biomass. The results imply that the sampling effort in Baltic Sea ice studies should be concentrated on scales of hundreds of meters to kilometers. Using the variations observed in the study area, the estimate for depth-integrated algal biomass in landfast sea ice in the Gulf of Finland (March 2003) is 5.5±4.4 mg chl-a m−2.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cressie NAC (1993) Statistics for spatial data. Wiley, New York
Eicken H, Lange MA, Dieckmann GS (1991) Spatial variability of sea-ice properties in the northwestern Weddell Sea. J Geophys Res 96:10603–10615
Frankenstein G, Garner R (1967) Equations for determining the brine volume of sea ice from −0.5 to −22.9°C. J Glaciol 6:943–944
Giannelli V, Thomas DN, Haas C, Kattner G, Kennedy H, Dieckmann GS (2001) Behaviour of dissolved organic matter and inorganic nutrients during experimental formation of sea ice. Ann Glaciol 33:317–321
Gosselin M, Legendre L, Therriault J-L, Demers S, Rochet M (1986) Physical control of the horizontal patchiness of sea-ice microalgae. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 29:289–298
Granskog MA, Kaartokallio H, Shirasawa K (2003a) Nutrient status of Baltic Sea ice—evidence for control by snow-ice formation, ice permeability and ice algae. J Geophys Res 108(C8):3253. DOI 10.1029/2002JC001386
Granskog MA, Martma TA, Vaikmäe RA (2003b) Development, structure and composition of landfast sea ice in the northern Baltic Sea. J Glaciol 49:138–149
Granskog MA, Ehn J, Niemelä (2004a) Characteristics and potential impacts of under-ice river plumes in the seasonally ice-covered Bothnian Bay (Baltic Sea). J Mar Syst (in press)
Granskog MA, Leppäranta M, Kawamura T, Ehn J, Shirasawa K (2004b) Seasonal development of the properties and composition of landfast sea ice in the Gulf of Finland, the Baltic Sea. J Geophys Res 109(C2):C02020. DOI 10.1029/2003JC001874
Grasshoff K, Ehrhardt M, Kremling K (1983) Methods of seawater analysis, 2nd edn. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim
Haecky P, Jonsson S, Andersson A (1998) Influence of sea ice on the composition of the spring phytoplankton bloom in the northern Baltic Sea. Polar Biol 20:1–8
HELCOM (1988) Guidelines for the Baltic monitoring programme third stage. Part D. Biological determinands. Baltic Sea environmental proceedings no. 27D
Legendre L, Martineau M-J, Therriault J-C, Demers S (1992) Chlorophyll a biomass and growth of sea-ice microalgae along a salinity gradient (southeastern Hudson Bay, Canadian Arctic). Polar Biol 12:445–453
Leppäranta M, Manninen T (1988) The brine and gas content of sea ice with attention to low salinities and high temperatures. Internal Rep 88-2, Finnish Institute of Marine Research, Helsinki
Meiners K, Fehling J, Granskog MA, Spindler M (2002) Abundance, biomass and composition of biota in Baltic sea ice and underlying water (March 2000). Polar Biol 25:761–770
Norrman B, Andersson A (1994) Development of ice biota in a temperate sea area (Gulf of Bothnia). Polar Biol 14:531–537
Robineau R, Legendre L, Kishino M, Kudoh S (1997) Horizontal heterogeneity of microalgal biomass in the first-year sea ice of Saroma-ko Lagoon (Hokkaido, Japan). J Mar Syst 11:81–91
Rysgaard S, Kuhl M, Glud RN, Hansen JW (2001) Biomass, production and horizontal patchiness of sea ice algae in a high-Arctic fjord (Young Sound, NE Greenland). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 223:15–26
SAS (1999) SAS OnlineDoc version eight. SAS Institute Inc., Cary. http://v8doc.sas.com/sashtml
Swadling KM, Gibson JAE, Ritz DA, Nichols PD (1997) Horizontal patchiness in sympagic organisms of the Antarctic fast ice. Antarct Sci 9:399–406
Tucker WB, Gow AJ, Richter JA (1984) On small-scale horizontal variations of salinity in first year sea ice. J Geophys Res 89:6505–6514
UNESCO (1983) Algorithms for computation of fundamental properties of seawater, UNESCO Technical Paper. Mar Sci 44:1–58
Zar JH (1999) Biostatistical analysis, 4th edn. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Acknowledgements
The participants of the Finnish-German “Sea ice ecology” course (joint undertaking by the University of Helsinki and University of Kiel) are acknowledged for their aid in field work and sample processing. Tvärminne Zoological Station provided facilities for sample processing. Ilkka Lastumäki and Kirsi Hyvärinen at FIMR made the nutrient analyses and Dylan Evans made the DOC measurements at UWB. Jouni Vainio provided radar images and interpretations of ice conditions. Suggestions made by three anonymous referees improved the manuscript. The editorial aid of Rolf Gradinger is also acknowledged. The Academy of Finland, the Walter and Andrée de Nottbeck Foundation and the Jenny and Antti Wihuri Foundation granted support for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Granskog, M.A., Kaartokallio, H., Kuosa, H. et al. Scales of horizontal patchiness in chlorophyll a, chemical and physical properties of landfast sea ice in the Gulf of Finland (Baltic Sea). Polar Biol 28, 276–283 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-004-0690-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-004-0690-5