Abstract
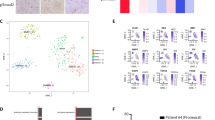
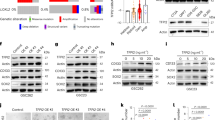
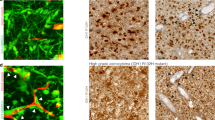
Glioblastoma (GBM) is a primary brain cancer that contains populations of stem-like cancer cells (GSCs) that home to specialized perivascular niches. GSC interactions with their niche influence self-renewal, differentiation and drug resistance, although the pathways underlying these events remain largely unknown. Here, we report that the integrin αvβ8 and its latent transforming growth factor β1 (TGFβ1) protein ligand have central roles in promoting niche co-option and GBM initiation. αvβ8 integrin is highly expressed in GSCs and is essential for self-renewal and lineage commitment in vitro. Fractionation of β8high cells from freshly resected human GBM samples also reveals a requirement for this integrin in tumorigenesis in vivo. Whole-transcriptome sequencing reveals that αvβ8 integrin regulates tumor development, in part, by driving TGFβ1-induced DNA replication and mitotic checkpoint progression. Collectively, these data identify the αvβ8 integrin-TGFβ1 signaling axis as crucial for exploitation of the perivascular niche and identify potential therapeutic targets for inhibiting tumor growth and progression in patients with GBM.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcantara Llaguno S, Chen J, Kwon CH, Jackson EL, Li Y, Burns DK et al. Malignant astrocytomas originate from neural stem/progenitor cells in a somatic tumor suppressor mouse model. Cancer cell 2009; 15: 45–56.
Zheng H, Ying H, Yan H, Kimmelman AC, Hiller DJ, Chen AJ et al. p53 and Pten control neural and glioma stem/progenitor cell renewal and differentiation. Nature 2008; 455: 1129–1133.
Lathia JD, Mack SC, Mulkearns-Hubert EE, Valentim CL, Rich JN . Cancer stem cells in glioblastoma. Genes Dev 2015; 29: 1203–1217.
Sanai N, Alvarez-Buylla A, Berger MS . Neural stem cells and the origin of gliomas. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 811–822.
Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q, Hjelmeland AB et al. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 2006; 444: 756–760.
Singh SK, Hawkins C, Clarke ID, Squire JA, Bayani J, Hide T et al. Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature 2004; 432: 396–401.
Gilbertson RJ, Rich JN . Making a tumour's bed: glioblastoma stem cells and the vascular niche. Nat Rev Cancer 2007; 7: 733–736.
Jain RK, di Tomaso E, Duda DG, Loeffler JS, Sorensen AG, Batchelor TT . Angiogenesis in brain tumours. Nat Rev Neurosci 2007; 8: 610–622.
Hynes RO . The extracellular matrix: not just pretty fibrils. Science 2009; 326: 1216–1219.
McCarty JH . Cell adhesion and signaling networks in brain neurovascular units. Curr Opin Hematol 2009; 16: 209–214.
Delamarre E, Taboubi S, Mathieu S, Berenguer C, Rigot V, Lissitzky JC et al. Expression of integrin alpha6beta1 enhances tumorigenesis in glioma cells. Am J Pathol 2009; 175: 844–855.
Lathia JD, Gallagher J, Heddleston JM, Wang J, Eyler CE, Macswords J et al. Integrin alpha 6 regulates glioblastoma stem cells. Cell Stem cell 2010; 6: 421–432.
Weis SM, Cheresh DA . alphaV integrins in angiogenesis and cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2011; 1: a006478.
Kanamori M, Vanden Berg SR, Bergers G, Berger MS, Pieper RO . Integrin beta3 overexpression suppresses tumor growth in a human model of gliomagenesis: implications for the role of beta3 overexpression in glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 2751–2758.
Gilbert MR, Kuhn J, Lamborn KR, Lieberman F, Wen PY, Mehta M et al. Cilengitide in patients with recurrent glioblastoma: the results of NABTC 03-02, a phase II trial with measures of treatment delivery. J Neurooncol 2012; 106: 147–153.
Nishimura SL, Sheppard D, Pytela R . Integrin alpha v beta 8. Interaction with vitronectin and functional divergence of the beta 8 cytoplasmic domain. J Biol Chem 1994; 269: 28708–28715.
Venstrom K, Reichardt L . Beta 8 integrins mediate interactions of chick sensory neurons with laminin-1, collagen IV, and fibronectin. Mol Biol Cell 1995; 6: 419–431.
Cambier S, Gline S, Mu D, Collins R, Araya J, Dolganov G et al. Integrin alpha(v)beta8-mediated activation of transforming growth factor-beta by perivascular astrocytes: an angiogenic control switch. Am J Pathol 2005; 166: 1883–1894.
Worthington JJ, Klementowicz JE, Travis MA . TGFbeta: a sleeping giant awoken by integrins. Trends Biochem Sci 2010; 36: 47–54.
Robertson IB, Rifkin DB . Regulation of the bioavailability of TGF-beta and TGF-beta-related proteins. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2016; 8: 6.
Allinson KR, Lee HS, Fruttiger M, McCarty JH, Arthur HM . Endothelial expression of TGFbeta type II receptor is required to maintain vascular integrity during postnatal development of the central nervous system. PLoS One 2012; 7: e39336.
Arnold TD, Ferrero GM, Qiu H, Phan IT, Akhurst RJ, Huang EJ et al. Defective retinal vascular endothelial cell development as a consequence of impaired integrin alphaVbeta8-mediated activation of transforming growth factor-beta. J Neurosci 2012; 32: 1197–1206.
Arnold TD, Niaudet C, Pang MF, Siegenthaler J, Gaengel K, Jung B et al. Excessive vascular sprouting underlies cerebral hemorrhage in mice lacking alphaVbeta8-TGFbeta signaling in the brain. Development 2014; 141: 4489–4499.
Hirota S, Clements TP, Tang LK, Morales JE, Lee HS, Oh SP et al. Neuropilin 1 balances beta8 integrin-activated TGFbeta signaling to control sprouting angiogenesis in the brain. Development 2015; 142: 4363–4373.
Nguyen HL, Lee YJ, Shin J, Lee E, Park SO, McCarty JH et al. TGF-beta signaling in endothelial cells, but not neuroepithelial cells, is essential for cerebral vascular development. Lab Invest 2011; 91: 1554–1563.
Proctor JM, Zang K, Wang D, Wang R, Reichardt LF . Vascular development of the brain requires beta8 integrin expression in the neuroepithelium. J Neuroscience 2005; 25: 9940–9948.
McCarty JH, Monahan-Earley RA, Brown LF, Keller M, Gerhardt H, Rubin K et al. Defective associations between blood vessels and brain parenchyma lead to cerebral hemorrhage in mice lacking alphav integrins. Mol Cell Biol 2002; 22: 7667–7677.
Ma L, Shen F, Jun K, Bao C, Kuo R, Young WL et al. Integrin beta8 deletion enhances vascular dysplasia and hemorrhage in the brain of adult Alk1 heterozygous mice. Transl Stroke Res 2016; 7: 488–496.
Su H, Kim H, Pawlikowska L, Kitamura H, Shen F, Cambier S et al. Reduced expression of integrin alphavbeta8 is associated with brain arteriovenous malformation pathogenesis. Am J Pathol 2010; 176: 1018–1027.
Dardiotis E, Siokas V, Zafeiridis T, Paterakis K, Tsivgoulis G, Dardioti M et al. Integrins AV and B8 gene polymorphisms and risk for intracerebral hemorrhage in Greek and Polish populations. Neuromol Med 2016; 19: 69–80.
Mobley AK, McCarty JH . beta8 integrin is essential for neuroblast migration in the rostral migratory stream. Glia 2011; 59: 1579–1587.
Mobley AK, Tchaicha JH, Shin J, Hossain MG, McCarty JH . Beta8 integrin regulates neurogenesis and neurovascular homeostasis in the adult brain. J Cell Sci 2009; 122: 1842–1851.
Patel AP, Tirosh I, Trombetta JJ, Shalek AK, Gillespie SM, Wakimoto H et al. Single-cell RNA-seq highlights intratumoral heterogeneity in primary glioblastoma. Science 2014; 344: 1396–1401.
Chaffer CL, Brueckmann I, Scheel C, Kaestli AJ, Wiggins PA, Rodrigues LO et al. Normal and neoplastic nonstem cells can spontaneously convert to a stem-like state. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2011; 108: 7950–7955.
Arrillaga-Romany I, Reardon DA, Wen PY . Current status of antiangiogenic therapies for glioblastomas. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2014; 23: 199–210.
Sathyan P, Zinn PO, Marisetty AL, Liu B, Kamal MM, Singh SK et al. Mir-21-Sox2 axis delineates glioblastoma subtypes with prognostic impact. J Neurosci 2015; 35: 15097–15112.
Wei J, Barr J, Kong LY, Wang Y, Wu A, Sharma AK et al. Glioma-associated cancer-initiating cells induce immunosuppression. Clin Cancer Res 2010; 16: 461–473.
Bruna A, Darken RS, Rojo F, Ocana A, Penuelas S, Arias A et al. High TGFbeta-Smad activity confers poor prognosis in glioma patients and promotes cell proliferation depending on the methylation of the PDGF-B gene. Cancer Cell 2007; 11: 147–160.
Penuelas S, Anido J, Prieto-Sanchez RM, Folch G, Barba I, Cuartas I et al. TGF-beta increases glioma-initiating cell self-renewal through the induction of LIF in human glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 2009; 15: 315–327.
Massague J . TGFbeta in cancer. Cell 2008; 134: 215–230.
Hirota S, Liu Q, Lee HS, Hossain MG, Lacy-Hulbert A, McCarty JH . The astrocyte-expressed integrin alphavbeta8 governs blood vessel sprouting in the developing retina. Development 2011; 138: 5157–5166.
Reyes SB, Narayanan AS, Lee HS, Tchaicha JH, Aldape KD, Lang FF et al. alphavbeta8 integrin interacts with RhoGDI1 to regulate Rac1 and Cdc42 activation and drive glioblastoma cell invasion. Mol Biol Cell 2013; 24: 474–482.
Tchaicha JH, Mobley AK, Hossain MG, Aldape KD, McCarty JH . A mosaic mouse model of astrocytoma identifies alphavbeta8 integrin as a negative regulator of tumor angiogenesis. Oncogene 2010; 29: 4460–4472.
Tchaicha JH, Reyes SB, Shin J, Hossain MG, Lang FF, McCarty JH . Glioblastoma angiogenesis and tumor cell invasiveness are differentially regulated by beta8 integrin. Cancer Research 2011; 71: 6371–6381.
Fang L, Deng Z, Shatseva T, Yang J, Peng C, Du WW et al. MicroRNA miR-93 promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis by targeting integrin-beta8. Oncogene 2011; 30: 806–821.
Huang JJ, Blobe GC . Dichotomous roles of TGF-beta in human cancer. Biochem Society Transac 2016; 44: 1441–1454.
Frei K, Gramatzki D, Tritschler I, Schroeder JJ, Espinoza L, Rushing EJ et al. Transforming growth factor-beta pathway activity in glioblastoma. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 5963–5977.
Rojas A, Padidam M, Cress D, Grady WM . TGF-beta receptor levels regulate the specificity of signaling pathway activation and biological effects of TGF-beta. Biochim Biophys Acta 2009; 1793: 1165–1173.
Nakajima H, Yonemura S, Murata M, Nakamura N, Piwnica-Worms H, Nishida E . Myt1 protein kinase is essential for Golgi and ER assembly during mitotic exit. J Cell Biol 2008; 181: 89–103.
Toledo CM, Ding Y, Hoellerbauer P, Davis RJ, Basom R, Girard EJ et al. Genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screens reveal Loss of redundancy between PKMYT1 and WEE1 in glioblastoma stem-like cells. Cell Rep 2015; 13: 2425–2439.
Ding Y, Hubert CG, Herman J, Corrin P, Toledo CM, Skutt-Kakaria K et al. Cancer-specific requirement for BUB1B/BUBR1 in human brain tumor isolates and genetically transformed cells. Cancer Discov 2013; 3: 198–211.
Nyati S, Schinske-Sebolt K, Pitchiaya S, Chekhovskiy K, Chator A, Chaudhry N et al. The kinase activity of the Ser/Thr kinase BUB1 promotes TGF-beta signaling. Science Signal 2015; 8: ra1.
Wee B, Pietras A, Ozawa T, Bazzoli E, Podlaha O, Antczak C et al. ABCG2 regulates self-renewal and stem cell marker expression but not tumorigenicity or radiation resistance of glioma cells. Sci Rep 2016; 6: 25956.
Anido J, Saez-Borderias A, Gonzalez-Junca A, Rodon L, Folch G, Carmona MA et al. TGF-beta receptor inhibitors target the CD44(high)/Id1(high) glioma-initiating cell population in human glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 2010; 18: 655–668.
Ferrara N, Hillan KJ, Gerber HP, Novotny W . Discovery and development of bevacizumab, an anti-VEGF antibody for treating cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2004; 3: 391–400.
Batchelor TT, Reardon DA, de Groot JF, Wick W, Weller M . Antiangiogenic therapy for glioblastoma: current status and future prospects. Clin Cancer Res 2014; 20: 5612–5619.
Bergers G, Hanahan D . Modes of resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2008; 8: 592–603.
Ellis LM, Reardon DA . Cancer: the nuances of therapy. Nature 2009; 458: 290–292.
Jahangiri A, De Lay M, Miller LM, Carbonell WS, Hu YL, Lu K et al. Gene expression profile identifies tyrosine kinase c-Met as a targetable mediator of antiangiogenic therapy resistance. Clin Cancer Res 2013; 19: 1773–1783.
Lu KV, Chang JP, Parachoniak CA, Pandika MM, Aghi MK, Meyronet D et al. VEGF inhibits tumor cell invasion and mesenchymal transition through a MET/VEGFR2 complex. Cancer Cell 2012; 22: 21–35.
McCarty JH . Glioblastoma resistance to anti-VEGF therapy: has the challenge been MET? Clin Cancer Res 2013; 19: 1631–1633.
Piao Y, Liang J, Holmes L, Henry V, Sulman E, de Groot JF . Acquired resistance to anti-VEGF therapy in glioblastoma is associated with a mesenchymal transition. Clin Cancer Res 2013; 19: 4392–4403.
Cheerathodi M, Avci NG, Guerrero PA, Tang LK, Popp J, Morales JE et al. The cytoskeletal adapter protein spinophilin regulates invadopodia dynamics and tumor cell invasion in glioblastoma. Mol Cancer Res 2016; 14: 1277–1287.
Lee HS, Cheerathodi M, Chaki SP, Reyes SB, Zheng Y, Lu Z et al. Protein tyrosine phosphatase-PEST and beta8 integrin regulate spatiotemporal patterns of RhoGDI1 activation in migrating cells. Mol Cell Biol 2015; 35: 1401–1413.
Upadhyaya M, Spurlock G, Thomas L, Thomas NS, Richards M, Mautner VF et al. Microarray-based copy number analysis of neurofibromatosis type-1 (NF1)-associated malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors reveals a role for Rho-GTPase pathway genes in NF1 tumorigenesis. Hum Mutat 2012; 33: 763–776.
Schittenhelm J, Klein A, Tatagiba MS, Meyermann R, Fend F, Goodman SL et al. Comparing the expression of integrins alphavbeta3, alphavbeta5, alphavbeta6, alphavbeta8, fibronectin and fibrinogen in human brain metastases and their corresponding primary tumors. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013; 6: 2719–2732.
Hamidi H, Pietila M, Ivaska J . The complexity of integrins in cancer and new scopes for therapeutic targeting. Br J Cancer 2016; 115: 1017–1023.
Vaillant F, Asselin-Labat ML, Shackleton M, Forrest NC, Lindeman GJ, Visvader JE . The mammary progenitor marker CD61/beta3 integrin identifies cancer stem cells in mouse models of mammary tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 7711–7717.
Ming XY, Fu L, Zhang LY, Qin YR, Cao TT, Chan KW et al. Integrin alpha7 is a functional cancer stem cell surface marker in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Commun 2016; 7: 13568.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank colleagues in the M.D. Anderson Neurosurgery department for providing freshly resected human samples. This work was supported by grants to JHM from NIH/NINDS (R01NS0 7635 and R01NS078402), the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (RP140411), and in part by an NIH/NCI SPORE in Brain Cancer (P50CA127001).
Author contributions
PAG, JHT, ZC, JEM, QG, EPS and NM performed critical experiments. FFL, GR and GF contributed important experimental reagents. PAG and JHM wrote the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guerrero, P., Tchaicha, J., Chen, Z. et al. Glioblastoma stem cells exploit the αvβ8 integrin-TGFβ1 signaling axis to drive tumor initiation and progression. Oncogene 36, 6568–6580 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.248
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.248
This article is cited by
-
IFITM3 promotes glioblastoma stem cell-mediated angiogenesis via regulating JAK/STAT3/bFGF signaling pathway
Cell Death & Disease (2024)
-
The U2AF65/circNCAPG/RREB1 feedback loop promotes malignant phenotypes of glioma stem cells through activating the TGF-β pathway
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
Paradoxical role of β8 integrin on angiogenesis and vasculogenic mimicry in glioblastoma
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
A Conceptual Framework for Inducing T Cell-Mediated Immunity Against Glioblastoma
Seminars in Immunopathology (2022)
-
Integrins regulate stemness in solid tumor: an emerging therapeutic target
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2021)