Abstract
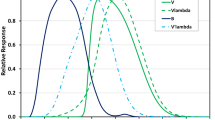
We report measurements from which we determine the spatial structure of the lunar contribution to night sky brightness, taken at the LSST site on Cerro Pachon in Chile. We use an array of six photodiodes with filters that approximate the Large Synoptic Survey Telescope’s u, g, r, i, z, and y bands. We use the sun as a proxy for the moon, and measure sky brightness as a function of zenith angle of the point on sky, zenith angle of the sun, and angular distance between the sun and the point on sky. We make a correction for the difference between the illumination spectrum of the sun and the moon. Since scattered sunlight totally dominates the daytime sky brightness, this technique allows us to cleanly determine the contribution to the (cloudless) night sky from backscattered moonlight, without contamination from other sources of night sky brightness. We estimate our uncertainty in the relative lunar night sky brightness vs. zenith and lunar angle to be between 0.3–0.7 mags depending on the passband. This information is useful in planning the optimal execution of the LSST survey, and perhaps for other astronomical observations as well. Although our primary objective is to map out the angular structure and spectrum of the scattered light from the atmosphere and particulates, we also make an estimate of the expected number of scattered lunar photons per pixel per second in LSST, and find values that are in overall agreement with previous estimates.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astrodon: Astrodon photometrics sloan filters. Accessed: 2016-01-09 (2015). http://www.astrodon.com/sloan.html
Holben, B.N., et al.: Aeronet - a federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 66(1), 1–16 (1998). doi:10.1016/S0034-4257(98)00031-5. ISSN 0034-4257
Chéreau, F.: Stellarium. Accessed: 2016-01-09 (2014). http://www.stellarium.org/
Coughlin, M., Claver, C.F., Stubbs, C., Tonry, J.L.: Optical All-Sky Camera for the Large Synoptic Survey Telescope. In: American Astronomical Society Meeting Abstracts #224, volume 224 of American Astronomical Society Meeting Abstracts, p #122.17 (2014)
Delgado, F., Saha, A., Chandrasekharan, S., Cook, K., Petry, C., Ridgway, S.: The LSST operations simulator. In: Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series, volume 9150 of Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series, p 915015 (2014), doi:10.1117/12.2056898
Chromey, F.R., Hasselbacher, D.A.: The flat sky: calibration and background uniformity in wide field astronomical images. PASP 108, 944 (1996). doi:10.1086/133817
High, F.W., Stubbs, C.W., Stalder, B., Gilmore, D.K., Tonry, J.L.: Sky variability in the y band at the LSST site. PASP 122, 722–730 (2010). doi:10.1086/653715
Ivezic, Z., Tyson, J.A., Abel, B., Acosta, E., Allsman, R., AlSayyad, Y., Anderson, S.F., Andrew, J., Angel, R., Angeli, G., Ansari, R., Antilogus, P., Arndt, K.T., Astier, P., Aubourg, E., Axelrod, T., Bard, D.J., Barr, J.D., Barrau, A., Bartlett, J.G., Bauman, B.J., Beaumont, S., Becker, A.C., Becla, J., Beldica, C., Bellavia, S., Blanc, G., Blandford, R.D., Bloom, J.S., Bogart, J., Borne, K., Bosch, J.F., Boutigny, D., Brandt, W.N., Brown, M.E., Bullock, J.S., Burchat, P., Burke, D.L., Cagnoli, G., Calabrese, D., Chandrasekharan, S., Chesley, S., Cheu, E.C., Chiang, J., Claver, C.F., Connolly, A.J., Cook, K.H., Cooray, A., Covey, K.R., Cribbs, C., Cui, W., Cutri, R., Daubard, G., Daues, G., Delgado, F., Digel, S., Doherty, P., Dubois, R., Dubois-Felsmann, G.P., Durech, J., Eracleous, M., Ferguson, H., Frank, J., Freemon, M., Gangler, E., Gawiser, E., Geary, J.C., Gee, P., Geha, M., Gibson, R.R., Gilmore, D.K., Glanzman, T., Goodenow, I., Gressler, W.J., Gris, P., Guyonnet, A., Hascall, P.A., Haupt, J., Hernandez, F., Hogan, C., Huang, D., Huffer, M.E., Innes, W.R., Jacoby, S.H., Jain, B., Jee, J., Jernigan, J.G., Jevremovic, D., Johns, K., Jones, R.L., Juramy-Gilles, C., Juric, M., Kahn, S.M., Kalirai, J.S., Kallivayalil, N., Kalmbach, B., Kantor, J.P., Kasliwal, M.M., Kessler, R., Kirkby, D., Knox, L., Kotov, I., Krabbendam, V.L., Krughoff, S., Kubanek, P., Kuczewski, J., Kulkarni, S., Lambert, R., Le Guillou, L., Levine, D., Liang, M., Lim, K., Lintott, C., Lupton, R.H., Mahabal, A., Marshall, P., Marshall, S., May, M., McKercher, R., Migliore, M., Miller, M., Mills, D.J., Monet, D.G., Moniez, M., Neill, D.R., Nief, J., Nomerotski, A., Nordby, M., O’Connor, P., Oliver, J., Olivier, S.S., Olsen, K., Ortiz, S., Owen, R.E., Pain, R., Peterson, J.R., Petry, C.E., Pierfederici, F., Pietrowicz, S., Pike, R., Pinto, P.A., Plante, R., Plate, S., Price, P.A., Prouza, M., Radeka, V., Rajagopal, J., Rasmussen, A., Regnault, N., Ridgway, S.T., Ritz, S., Rosing, W., Roucelle, C., Rumore, M.R., Russo, S., Saha, A., Sassolas, B., Schalk, T.L., Schindler, R.H., Schneider, D.P., Schumacher, G., Sebag, J., Sembroski, G.H., Seppala, L.G., Shipsey, I., Silvestri, N., Smith, J.A., Smith, R.C., Strauss, M.A., Stubbs, C.W., Sweeney, D., Szalay, A., Takacs, P., Thaler, J.J., Van Berg, R., Vanden Berk, D., Vetter, K., Virieux, F., Xin, B., Walkowicz, L., Walter, C.W., Wang, D.L., Warner, M., Willman, B., Wittman, D., Wolff, S.C., Wood-Vasey, W.M., Yoachim, P., Zhan, H., for the LSST Collaboration: LSST: from Science Drivers to Reference Design and Anticipated Data Products. ArXiv e-prints (2008)
Jones, A., Noll, S., Kausch, W., Szyszka, C., Kimeswenger, S.: An advanced scattered moonlight model for Cerro Paranal. A&A 560, A91 (2013). doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201322433
Jones, A., Noll, S., Kausch, W., Kimeswenger, S.: An Advanced Scattered Moonlight Model. In: American Astronomical Society Meeting Abstracts #224, volume 224 of American Astronomical Society Meeting Abstracts, p #405.03 (2014)
Krisciunas, K., Schaefer, B.: A model of the brightness of moonlight. Astronomical Society of the Pacific 103, 1033–1039 (1991). doi:10.1086/132921
Kieffer, H.H., Stone, T.C.: The Spectral Irradiance of the Moon. AJ 129, 2887–2901 (2005). doi:10.1086/430185
Noll, S., Kausch, W., Barden, M., Jones, A.M., Szyszka, C., Kimeswenger, S., Vinther, J.: An atmospheric radiation model for Cerro Paranal. I. The optical spectral range. A&A 543, A92 (2012). doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201219040
Stubbs, C.W., High, F.W., George, M.R., DeRose, K.L., Blondin, S., Tonry, J.L., Chambers, K.C., Granett, B.R., Burke, D.L., Smith, R.C.: Toward more precise survey photometry for PanSTARRS and LSST: measuring directly the optical transmission spectrum of the atmosphere. PASP 119, 1163–1178 (2007). doi:10.1086/522208
Walker, A.: Noao newsletter. NOAO Newsletter 10, 16 (1987)
Winkler, H., van Wyk, F., Marang, F.: South African night sky brightness during high aerosol epochs. ArXiv e-prints (2014)
Acknowledgments
MC was supported by the National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship Program, under NSF grant number DGE 1144152. CWS is grateful to the DOE Office of Science for their support under award DE-SC0007881. Thanks also to Prof. Gary Swensen of Univ. of Illinois for hospitality in the ALO building at Pachon. We would also like to thank Dr. Tom Stone and an anonymous referee for comprehensive comments on an initial version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coughlin, M., Stubbs, C. & Claver, C. A daytime measurement of the lunar contribution to the night sky brightness in LSST’s ugrizy bands–initial results. Exp Astron 41, 393–408 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10686-016-9494-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10686-016-9494-1