Abstract
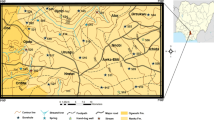
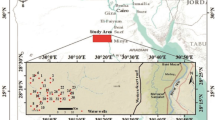
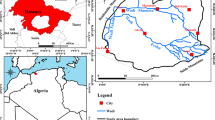
The Lower Volta River Basin of Ghana is an important international and local tourism destination. Communities in the basin depend on shallow aquifer systems, the Volta River, and nearby streams as their sources of water for domestic purposes, cattle watering, and irrigation. Due to increasing human activities and limited information on water quality in the area, a holistic assessment of the quality of the water resources in the basin was conducted using hydrochemistry, δ2H and δ18O, principal components analysis, and selected indices. EC ranged from 141 to 19,370 μS/cm and 60.9–986 μS/cm for shallow groundwater and surface water respectively. NO3− levels above 45–1049.9 mg/l were observed in 45% of analyzed wells. Na–Cl- and HCO3–Ca-dominant facies are identified. Silicate weathering, evaporite dissolution, cation exchange, and salinity are the hydrochemical processes influencing the shallow groundwater in the area. δ2H–δ18O‰ plot showed meteoric shallow groundwater recharge. Ion ratios, EC, and Cl− versus δ18O‰ relationships suggest dissolution and seawater intrusion as causes of groundwater salinity. Hydrochemistry, principal components analyses, and NO3− versus δ18O showed evidence of anthropogenic pollution on water in the basin. All analyzed surface water and 79% of well samples were within suitable range for irrigation. Based on the CCMEWQI model criteria, 85% of the surface water were in good-to-excellent categories while majority of the shallow groundwater were in fair, marginal, and poor categories. The combined approach provided vital information on water quality in the basin. Strategic control measures were proposed.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas, Z., Su, C., Tahira, F., Mapoma, H. W. T., & Aziz, S. Z. (2015). Quality and hydrochemistry of groundwater used for drinking in Lahore, Pakistan: Analysis of source and distributed groundwater. Environmental Earth Sciences,74(5), 4281–4294.
Abdul-Razak, A., Asiedu, A. B., & Entsua-Mensah, R. E. M. (2009). Assessment of the water quality of the Oti River in Ghana. West African Journal of Applied Ecology,15, 1–12.
Abin, A., Sibin, R., Aghil, T. B., Magesh, N. S., & Sridhar, S. G. D. (2014). Statistical evaluation of groundwater geochemistry: A case study between Chinnakuppam and Kulathur, South Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India. Journal of Coastal Sciences,1(1), 58–62.
Acheampong, S. Y., & Hess, J. W. (1998). Hydrogeological and hydrochemical framework of the shallow groundwater system in the southern Voltaian Sedimentary Basin, Ghana. Hydrogeology Journal, 6(4), 527–537.
Adams, S., Titus, R., Pietersen, K., Tredoux, G., & Harris, C. (2001). Hydrochemical characteristics of aquifers near Sutherland in the Western Karoo, South Africa. Journal of Hydrology,241(1), 91–103.
Adomako, D., Gibrilla, A., Maloszewski, P., Ganyaglo, S. Y., & Rai, S. P. (2015). Tracing stable isotopes (δ2H and δ18O) from meteoric water to groundwater in the Densu River basin of Ghana. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,187(5), 264.
Aghazadeh, N., & Mogaddam, A. A. (2010). Assessment of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural uses in the Oshnavieh area, Northwest of Iran. Journal of Environmental Protection,1(01), 30.
Akiti, T. T. (1982). Nitrate levels in some granitic aquifers from Ghana. In Proceedings of international symposium on impact of agricultural activities on groundwater (pp. 87–98).
Akiti, T. T. (1986). Environmental isotope study of ground water in crystalline rocks of the Accra plains, Ghana. Fourth working meeting isotopes in nature, proceedings of an advisory group meeting, IAEA, Vienna.
Akouvi, A., Dray, M., Violette, S., de Marsily, G., & Zuppi, G. M. (2008). The sedimentary coastal basin of Togo: Example of a multilayered aquifer still influenced by a palaeo-seawater intrusion. Hydrogeology Journal,16(3), 419–436.
Akpati, B. N. (1978). Geologic structure and evolution of the Keta basin, Ghana, West Africa. Geological Society of America Bulletin,89(1), 124–132.
Amiri, V., Sohrabi, N., & Dadgar, M. A. (2015). Evaluation of groundwater chemistry and its suitability for drinking and agricultural uses in the Lenjanat plain, central Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences,74(7), 6163–6176.
Amoah, C., & Koranteng, S. S. (2006). Volta Basin Research Project (VBRP). Legon: University of Ghana.
Anornu, G., Gibrilla, A., & Adomako, D. (2017). Tracking nitrate sources in groundwater and associated health risk for rural communities in the White Volta River basin of Ghana using isotopic approach (δ15N, δ18ONO3 and 3H). Science of The Total Environment, 603, 687–698.
Appelo, C. A. J., & Postma, D. (1993). Groundwater, geochemistry and pollution. Rotterdam: Balkema.
Appelo, C. A. J., & Postma, D. (1999). Chemical analysis of groundwater. Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution: AA Balkema/Rotterdam/Brookfield.
Appelo, C. A. J., & Postma, D. (2004). Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Asadi, S. S., Vuppala, P., & Reddy, M. A. (2007). Remote sensing and GIS techniques for evaluation of groundwater quality in municipal corporation of Hyderabad (Zone-V), India. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,4(1), 45–52.
Avornyo, V. K., Adjadeh, T. A., & Amatekpor, J. K. (2013). Pan Soils in the Lower Volta Basin of Ghana. West African Journal of Applied Ecology,21(2), 63–77.
Banoeng-Yakubo, B., Yidana, S. M., & Nti, E. (2009). Hydrochemical analysis of groundwater using multivariate statistical methods—The Volta region, Ghana. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering,13(1), 55–63.
Campbell, M. O. N. (2005). Sacred Groves for forest conservation in Ghana’s coastal savannas: Assessing ecological and social dimensions. Singapore Journal of Tropical Geography,26(2), 151–169.
Cary, L., Petelet-Giraud, E., Bertrand, G., Kloppmann, W., Aquilina, L., Martins, V., et al. (2015). Origins and processes of groundwater salinization in the urban coastal aquifers of Recife (Pernambuco, Brazil): A multi-isotope approach. Science of the Total Environment,530, 411–429.
Cerling, T. E., Pederson, B. L., & Von Damm, K. L. (1989). Sodium-calcium ion exchange in the weathering of shales: Implications for global weathering budgets. Geology,17(6), 552–554.
Coplen, T. B. (1988). Normalization of oxygen and hydrogen isotope data. Chemical Geology: Isotope Geoscience Section,72(4), 293–297.
Craig, H. (1961). Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science,133(3465), 1702–1703.
Deutsch, W. J., & Siegel, R. (1997). Groundwater geochemistry: Fundamentals and applications to contamination. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Dickson, K. B., & Benneh, G. A. (2004). New Geography of Ghana. London: Longmans Group Ltd.
Domenico, P. A., & Schwartz, F. W. (1998). Physical and chemical hydrogeology (Vol. 506). New York: Wiley.
Doneen, L. D. (1964). Notes on water quality in agriculture. Department of Water Science and Engineering: University of California, Davis.
Elumalai, V., Brindha, K., Sithole, B., & Lakshmanan, E. (2017). Spatial interpolation methods and geostatistics for mapping groundwater contamination in a coastal area. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,24(12), 11601–11617.
EPC-CS34, C.C.M.E., (1991). Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment. Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada.
Fernandes, P. G., Carreira, P., & da Silva, M. O. (2008). Anthropogenic sources of contamination recognition—Sines coastal aquifer (SW Portugal). Journal of Geochemical Exploration,98(1), 1–14.
Fianko, J. R., Nartey, V. K., & Donkor, A. (2010). The hydrochemistry of groundwater in rural communities within the Tema District. Ghana. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 168(1–4), 441–449.
Fisher, R. S., & Mullican, W. F., III. (1997). Hydrochemical evolution of sodium-sulfate and sodium-chloride groundwater beneath the northern Chihuahuan Desert, Trans-Pecos, Texas, USA. Hydrogeology Journal,5(2), 4–16.
Folk, R. L., & Land, L. S. (1975). Mg/Ca ratio and salinity: Two controls over crystallization of dolomite. AAPG bulletin,59(1), 60–68.
Freeze, R. A., & Cherry, J. A. (1979). Groundwater (Vol. 604, pp. 215–227). Englewood cliffs: Prentice Hall Inc.
Gampson, E. K., Nartey, V. K., Golow, A. A., & Akiti, T. T. (2014). Hydrochemical study of water collected at a section of the Lower Volta River (Akuse to Sogakope area), Ghana. Applied Water Science,4(2), 129–143.
Ganyaglo, S. Y., Banoeng-Yakubo, B., Osae, S., Dampare, S. B., Fianko, J. R., & Bhuiyan, M. A. (2010). Hydrochemical and isotopic characterisation of groundwater in Eastern Region of Ghana. Water Resour Protection,2, 199–208.
Ganyaglo, S. Y., Osae, S., Dampare, S. B., Fianko, J. R., Bhuiyan, M. A., Gibrilla, A., et al. (2012). Preliminary groundwater quality assessment in the central region of Ghana. Environmental Earth Sciences,66(2), 573–587.
Gaye, C. B. (2001). Isotope techniques for monitoring groundwater salinization. Hydrogeology Journal,9(3), 217–218.
Gibbs, R. J. (1970). Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science,170(3962), 1088–1090.
Gibrilla, A., Bam, E. K. P., Adomako, D., Ganyaglo, S., Osae, S., Akiti, T. T., et al. (2011). Application of water quality index (WQI) and multivariate analysis for groundwater quality assessment of the Birimian and Cape Coast Granitoid Complex: Densu River Basin of Ghana. Water Quality, Exposure and Health,3(2), 63.
Güler, C., Kurt, M. A., Alpaslan, M., & Akbulut, C. (2012). Assessment of the impact of anthropogenic activities on the groundwater hydrology and chemistry in Tarsus coastal plain (Mersin, SE plain Turkey) using fuzzy clustering, multivariate statistics and GIS techniques. Journal of Hydrology,414, 435–451.
Gumma, M. K., & Pavelic, P. (2013). Mapping of groundwater potential zones across Ghana using remote sensing, geographic information systems, and spatial modeling. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,185(4), 3561–3579.
Helena, B., Pardo, R., Vega, M., Barrado, E., Fernandez, J. M., & Fernandez, L. (2000). Temporal evolution of groundwater composition in an alluvial aquifer (Pisuerga River, Spain) by principal component analysis. Water Research,34(3), 807–816.
Helstrup, T. (2006). Environmental isotopic and hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater from the Cretaceous-Eocene limestone aquifer in the Keta Basin, Ghana, and the Coastal Sedimentary Basin of Togo (Doctoral dissertation, Ph. D. thesis).
Hem, J.D. (1985). Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water (Vol. 2254). Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey.
Hounslow, A. (1995). Water quality data: Analysis and interpretation. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Hurley, T., Sadiq, R., & Mazumder, A. (2012). Adaptation and evaluation of the Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment Water Quality Index (CCME WQI) for use as an effective tool to characterize drinking source water quality. Water Research,46(11), 3544–3552.
Jackson, J. E. (2005). A user’s guide to principal components (Vol. 587, pp. 150–166). New York: Wiley.
Jørgensen, N. O., & Banoeng-Yakubo, B. K. (2001). Environmental isotopes (18 O, 2 H, and 87 Sr/86 Sr) as a tool in groundwater investigations in the Keta Basin, Ghana. Hydrogeology Journal,9(2), 190–201.
Kaiser, H. F. (1960). The application of electronic computers to factor analysis. Educational and Psychological Measurement,20(1), 141–151.
Kaiser, H. F., & Rice, J. (1974). Little jiffy, mark IV. Educational and psychological measurement, 34(1), 111–117.
Kaka, E. A., Akiti, T. T., & Nartey, V. K. (2011). Stable isotopes of water as indicator of groundwater-Volta Lake interaction in the southwestern margin of the Volta Lake, Ghana. Elixir International Journal,39, 4888–4894.
Karikari, A. Y., Bernasko, J. K., & Bosque-Hamilton, E. K. A. (2007). An assessment of water quality of Angaw River in southeastern coastal plains of Ghana. West African Journal of Applied Ecology,11(1), 77–87.
Kazakis, N., Pavlou, A., Vargemezis, G., Voudouris, K. S., Soulios, G., Pliakas, F., et al. (2016). Seawater intrusion mapping using electrical resistivity tomography and hydrochemical data: An application in the coastal area of eastern Thermaikos Gulf, Greece. Science of the Total Environment,543, 373–387.
Kebede, S., Travi, Y., Alemayehu, T., & Ayenew, T. (2005). Groundwater recharge, circulation and geochemical evolution in the source region of the Blue Nile River, Ethiopia. Applied Geochemistry,20(9), 1658–1676.
Kelley, W. P. (1963). Use of saline irrigation water. Soil science, 95(6), 385–391.
Kesse, G. O. (1985). The mineral and rock resources of Ghana. Rotterdam: Balkema Publishers.
Khan, A. A., Paterson, R., & Khan, H. (2004). Modification and application of the Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment Water Quality Index (CCME WQI) for the communication of drinking water quality data in newfoundland and labrador. Water Quality Research Journal of Canada,39(3), 285–293.
Kim, J. H., Yum, B. W., Kim, R. H., Koh, D. C., Cheong, T. J., Lee, J., et al. (2003). Application of cluster analysis for the hydrogeochemical factors of saline groundwater in Kimje, Korea. Geosciences Journal,7(4), 313–322.
Koh, D. C., Chae, G. T., Yoon, Y. Y., Kang, B. R., Koh, G. W., & Park, K. H. (2009). Baseline geochemical characteristics of groundwater in the mountainous area of Jeju Island, South Korea: Implications for degree of mineralization and nitrate contamination. Journal of Hydrology,376(1), 81–93.
Kortatsi, B. K. (1994). Groundwater utilization in Ghana. IAHS Publications-Series of Proceedings and Reports of the International Association of Hydrological Sciences,222, 149–156.
Kortatsi, B. K., Young, E., & Mensah-Bonsu, A. (2005). Potential impact of large scale abstraction on the quality of shallow groundwater for irrigation in the Keta Strip, Ghana. West African Journal of Applied Ecology,8(1), 1–12.
Lee, J. Y., & Song, S. H. (2007). Evaluation of groundwater quality in coastal areas: Implications for sustainable agriculture. Environmental Geology,52(7), 1231–1242.
Lghoul, M., Maqsoud, A., Hakkou, R., & Kchikach, A. (2014). Hydrogeochemical behavior around the abandoned Kettara mine site, Morocco. Journal of Geochemical Exploration,144, 456–467.
Li, P. (2014). Research on groundwater environment under human interferences: A case study from Weining plain, Northwest China. Changan: Changan University (Doctoral Thesis).
Liu, C. Q., Li, S. L., Lang, Y. C., & Xiao, H. Y. (2006). Using δ15N-and δ18O-values to identify nitrate sources in karst ground water, Guiyang, Southwest China. Environmental Science and Technology,40(22), 6928–6933.
Menció, A., & Mas-Pla, J. (2008). Assessment by multivariate analysis of groundwater–surface water interactions in urbanized Mediterranean streams. Journal of Hydrology,352(3), 355–366.
Meybeck, M. (1979). Major elements contents of river waters and dissolved inputs to the oceans. Revue de Géologie dynamique et de Géographie physique, 21(3), 215–246.
Millero, F. J., Feistel, R., Wright, D. G., & McDougall, T. J. (2008). The composition of standard seawater and the definition of the reference-composition salinity scale. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers,55(1), 50–72.
Millero, F. J., & Sohn, M. J. (1996). Chemical oceanography. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press.
Moussa, A. B., Mzali, H., Zouari, K., & Hezzi, H. (2014). Hydrochemical and isotopic assessment of groundwater quality in the Quaternary shallow aquifer, Tazoghrane region, north-eastern Tunisia. Quaternary International,338, 51–58.
Moya, C. E., Raiber, M., Taulis, M., & Cox, M. E. (2015). Hydrochemical evolution and groundwater flow processes in the Galilee and Eromanga basins, Great Artesian Basin, Australia: A multivariate statistical approach. Science of the Total Environment,508, 411–426.
Mtoni, Y., Mjemah, I. C., Bakundukize, C., Van Camp, M., Martens, K., & Walraevens, K. (2013). Saltwater intrusion and nitrate pollution in the coastal aquifer of Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Environmental Earth Sciences,70(3), 1091–1111.
Mukherjee, A., & Fryar, A. E. (2008). Deeper groundwater chemistry and geochemical modeling of the arsenic affected western Bengal basin, West Bengal, India. Applied Geochemistry,23(4), 863–894.
Murkute, Y. A. (2014). Hydrogeochemical characterization and quality assessment of groundwater around Umrer coal mine area Nagpur District, Maharashtra, India. Environmental Earth Sciences,72(10), 4059–4073.
Nas, B., & Berktay, A. (2010). Groundwater quality mapping in urban groundwater using GIS. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,160(1), 215–227.
Nerquaye-Tetteh, B.H. (1993, September). Water, sanitation, environment and development: Water resources appraisal in the Keta Basin. In 19th WEDC Conference, Accra, Ghana.
Park, S. C., Yun, S. T., Chae, G. T., Yoo, I. S., Shin, K. S., Heo, C. H., et al. (2005). Regional hydrochemical study on salinization of coastal aquifers, western coastal area of South Korea. Journal of Hydrology,313(3–4), 182–194.
Parkhurst, D. L., & Appelo, C. A. J. (1999). User’s guide to PHREEQC (Version 2): A computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations.
Piper, A. M. (1944). A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union,25(6), 914–928.
Plummer, L. N., Busby, J. F., Lee, R. W., & Hanshaw, B. B. (1990). Geochemical modeling of the Madison aquifer in parts of Montana, Wyoming, and South Dakota. Water Resources Research,26(9), 1981–2014.
Pulido-Leboeuf, P. (2004). Seawater intrusion and associated processes in a small coastal complex aquifer (Castell de Ferro, Spain). Applied Geochemistry,19(10), 1517–1527.
Qian, C., Wu, X., Mu, W. P., Fu, R. Z., Zhu, G., Wang, Z. R., et al. (2016). Hydrogeochemical characterization and suitability assessment of groundwater in an agro- pastoral area, Ordos Basin, NW China. Environmental Earth Sciences,75(20), 1356.
Ramesh, K., & Elango, L. (2012). Groundwater quality and its suitability for domestic and agricultural use in Tondiar river basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,184(6), 3887–3899.
Raghunath, H. M. (1987). Geochemical survey and water quality (pp. 343–347). New Delhi: Groundwater Wiley eastern limited.
Rao, N. S. (1997). The occurrence and behaviour of fluoride in the groundwater of the Lower Vamsadhara River basin. India. Hydrological sciences journal, 42(6), 877–892.
Rao, N. S. (2008). Factors controlling the salinity in groundwater in parts of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh. India. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 138(1–3), 327–341.
Rengasamy, P., & Marchuk, A. (2011). Cation ratio of soil structural stability (CROSS). Soil Research,49(3), 280–285.
Richards, L. A. (1954). Improvement and management of soils in arid and semi-arid regions in relation to salinity and alkalinity. Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. USDA Handbook, 60, 34–54.
Saka, D., Akiti, T. T., Osae, S., Appenteng, M. K., & Gibrilla, A. (2013). Hydrogeochemistry and isotope studies of groundwater in the Ga West Municipal Area, Ghana. Applied Water Science,3(3), 577–588.
Salem, Z. E., Atwia, M. G., & El-Horiny, M. M. (2015). Hydrogeochemical analysis and evaluation of groundwater in the reclaimed small basin of Abu Mina, Egypt. Hydrogeology Journal,23(8), 1781–1797.
Selvakumar, S., Chandrasekar, N., Kaliraj, S., & Magesh, N. S. (2017). Salinization of shallow aquifer in the Karamaniyar river basin (pp. 1–19). Environment, Development and Sustainability: Southern India.
Şener, Ş., Şener, E., & Davraz, A. (2017). Evaluation of water quality using water quality index (WQI) method and GIS in Aksu River (SW-Turkey). Science of the Total Environment,584, 131–144.
Silva-Filho, E. V., Barcellos, R. G. S., Emblanch, C., Blavoux, B., Sella, S. M., Daniel, M., et al. (2009). Groundwater chemical characterization of a Rio de Janeiro coastal aquifer, SE Brazil. Journal of South American Earth Sciences,27(1), 100–108.
Simler, R. (2009). DIAGRAMMES: Logiciel d’hydrochimie multilangage en distribution libre. France: Laboratoire d’Hydrogéologie d’Avignon.
Singh, A. K., Mondal, G. C., Kumar, S., Singh, T. B., Tewary, B. K., & Sinha, A. (2008). Major ion chemistry, weathering processes and water quality assessment in upper catchment of Damodar River basin. India. Environmental geology, 54(4), 745–758.
Singh, E. J., Gupta, A., & Singh, N. R. (2013). Groundwater quality in Imphal West district, Manipur, India, with multivariate statistical analysis of data. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,20(4), 2421–2434.
Singh, K. P., Malik, A., & Sinha, S. (2005). Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources of Gomti river (India) using multivariate statistical techniques—A case study. Analytica Chimica Acta,538(1), 355–374.
Smith, C. J., Oster, J. D., & Sposito, G. (2015). Potassium and magnesium in irrigation water quality assessment. Agricultural Water Management,157, 59–64.
Szabolcs, I., & Darab, C. (1964). The influence of irrigation water of high sodium carbonate content of soils. In Proceedings of 8th international congress of ISSS, Trans, II (pp. 803–812).
Turekian, K. K., (1977). Geochemical distribution of elements. Encyclopedia of science and technology, 4, 627–630.
Thyne, G., Güler, C., & Poeter, E. (2004). Sequential analysis of hydrochemical data for watershed characterization. Ground Water,42(5), 711–723.
Vasanthavigar, M., Srinivasamoorthy, K., Ganthi, R. R., Vijayaraghavan, K., & Sarma, V. S. (2012). Characterisation and quality assessment of groundwater with a special emphasis on irrigation utility: Thirumanimuttar sub-basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences,5(2), 245–258.
Vengosh, A., Spivack, A. J., Artzi, Y., & Ayalon, A. (1999). Geochemical and boron, strontium, and oxygen isotopic constraints on the origin of the salinity in groundwater from the Mediterranean coast of Israel. Water Resources Research,35(6), 877–1894.
Vetrimurugan, E., Elango, L., & Rajmohan, N. (2013). Sources of contaminants and groundwater quality in the coastal part of a river delta. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 10(3), 473–486.
Wang, Y. (2011). Isotopic and hydrogeochemical studies of the coast aquifer-aquitard system in the Pearl River Delta, China. 香港大學學位論文, 1–0.
Water Resources Commission—Water Research Institute Report. (2015). Report on improving access to potable water supply for downstream communities of the Volta Lake. Technical Report, Water Resources Commission (WRC)—Water Research Institute Report (WRI), Accra.
Who, G. (2011). Guidelines for drinking-water quality. World Health Organization,216, 303–304.
Wilcox, L. (1955). Classification and uses of irrigation waters. USDA Circular No. 969, Washington, DC.
Williams, B., Onsman, A., & Brown, T. (2010). Exploratory factor analysis: A five-step guide for novices. Australasian Journal of Paramedicine,8(3), 1–13.
Wirmvem, M. J., Ohba, T., Fantong, W. Y., Ayonghe, S. N., Suila, J. Y., Asaah, A. N. E., et al. (2013). Hydrochemistry of shallow groundwater and surface water in the Ndop plain, North West Cameroon. African Journal of Environmental Science and Technology,7(6), 518–530.
Wu, Z., Wang, X., Chen, Y., Cai, Y., & Deng, J. (2018). Assessing river water quality using water quality index in Lake Taihu Basin, China. Science of the Total Environment,612, 914–922.
Xiao, J., Jin, Z. D., Wang, J., & Zhang, F. (2015). Hydrochemical characteristics, controlling factors and solute sources of groundwater within the Tarim River Basin in the extreme arid region, NW Tibetan Plateau. Quaternary International,380, 237–246.
Yang, Q., Li, Z., Ma, H., Wang, L., & Martín, J. D. (2016). Identification of the hydrogeochemical processes and assessment of groundwater quality using classic integrated geochemical methods in the Southeastern part of Ordos basin, China. Environmental Pollution,218, 879–888.
Yidana, S. M. (2010). Groundwater classification using multivariate statistical methods: Southern Ghana. Journal of African Earth Sciences,57(5), 455–469.
Yidana, S. M., Ophori, D., & Banoeng-Yakubo, B. (2008). Hydrogeological and hydrochemical characterization of the Voltaian Basin: The Afram Plains area, Ghana. Environmental Geology,53(6), 1213–1223.
Yidana, S. M., Ophori, D., & Obeng, B. (2007). Hydrochemical analysis of groundwater from the Keta Basin, Ghana. Journal of Environmental Hydrology,15, 1–11.
Zhang, B., Song, X., Zhang, Y., Han, D., Tang, C., Yu, Y., et al. (2012). Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality assessment of surface water and groundwater in Songnen plain, Northeast China. Water Research,46(8), 2737–2748.
Acknowledgements
This paper forms part of the PhD research of the corresponding author. The study was funded by the Regional Water and Environmental Sanitation Centre, Kumasi (RWESCK) with funding from Ghana Government and the World Bank under the Africa Centre’s of Excellence project. The views expressed in this paper do not reflect those of the World Bank, Ghana Government and KNUST. The authors acknowledge the IAEA, the Director of National Institute of Hydrology and staff of the Nuclear Hydrology Laboratory Roorkee, India, and the Ghana Atomic Energy Commission for samples analysis and logistic supports. We also thank the editor and anonymous reviewers for their contributions in enriching the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Egbi, C.D., Anornu, G., Appiah-Adjei, E.K. et al. Evaluation of water quality using hydrochemistry, stable isotopes, and water quality indices in the Lower Volta River Basin of Ghana. Environ Dev Sustain 21, 3033–3063 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-018-0180-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-018-0180-5