Abstract
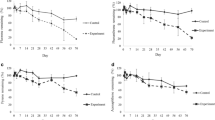
A microcosm experiment was used to examine (1) the effects of different bioremediation schemes on degradation of anthracene and the structure of free-living marine nematodes in a lightly contaminated (4.5 μg g−1) sediment from Bizerte lagoon and (2) the responses of the nematode community upon an artificial spiking of a low dose anthracene (1 μg g−1). For that purpose sediment microcosms were incubated in laboratory for 40 days. Bioremediation techniques decreased the anthracene contamination, and interestingly, biodegradation were more efficient when anthracene was artificial supplied into the sediment suggesting that the addition of bioavailable anthracene stimulated the bacterial community to adjust towards a PAH-degrading community. Spiking with this low dose of anthracene provoked significant changes in the nematode community structure and abundance, with the elimination of specific species such as Mesacanthion diplechma, the decrease of the dominant species Oncholaimus campylocercoides and the increase in abundance of opportunistic species such as Spirinia parasitifera. This would suggest a low tolerance of the nematode community despite the presence of a weak anthracene contamination in the sediment that could have allow dominance of an anthracene tolerant nematode species. Anthracene toxicity was alleviated in biostimulation treatments, leading to a strong increase in nematode abundance, concomitantly with changes in the nematode community structure; Prochromadorella neapolitana became the most abundant species.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbondanzi F, Bruzzi L, Campisi T, Frezzati A, Guerra R, Lacondini A (2006) Biotreatability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in brackish sediments: preliminary studies of an integrated monitoring. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 57(4):214–221
Agarry SE, Owabor CN (2011) Anaerobic bioremediation of marine sediment artificially contaminated with anthracene and naphthalene. Environ Technol 32(12):1375–1381
Alexander M (2000) Aging, bioavailability, and overestimation of risk from environmental pollutants. Environ Sci Technol 34(20):4259–4265
Atlas R, Bragg J (2009) Bioremediation of marine oil spills: when and when not—the Exxon Valdez experience. Microb Biotechnol 2(2):213–221
Austen MC (2004). Natural nematode communities are useful tools to address ecological and applied questions. In: Proceeding of the fourth international congress of nematology, vol 2. Leiden, E J Brill, pp 775–791
Austen MC, McEvoy AJ (1997) The use of offshore meiobenthic communities in laboratory microcosm experiments: response to heavy metal contamination. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 211(2):247–261
Ben Said O, Goni-Urriza MS, El Bour M, Dellali M, Aissa P, Duran R (2008) Characterization of aerobic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria from Bizerte lagoon sediments, Tunisia. J Appl Microbiol 104(4):987–997
Ben Said O, Goni-Urriza M, El Bour M, Aissa P, Duran R (2010) Bacterial community structure of sediments of the Bizerte lagoon (Tunisia), a southern Mediterranean coastal anthropized lagoon. Microb Ecol 59(3):445–456
Beyrem H, Aissa P (2000) Free-living nematodes, bio-indicators of the evolution of hydrocarbon concentrations in the bay of Bizerta (Tunisia). Cah Biol Mar 41(3):329–342
Beyrem H, Mahmoudi E, Essid N, Hedfi A, Boufahja F, Aissa P (2007) Individual and combined effects of cadmium and diesel on a nematode community in a laboratory microcosm experiment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 68(3):412–418
Beyrem H, Louati H, Essid N, Aissa P, Mahmoudi E (2010) Effects of two lubricant oils on marine nematode assemblages in a laboratory microcosm experiment. Mar Environ Res 69(4):248–253
Blanck H (2002) A critical review of procedures and approaches used for assessing pollution-induced community tolerance (PICT) in biotic communities. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 8(5):1003–1034
Bongers T, Ferris H (1999) Nematode community structure as a bioindicator in environmental monitoring. Trends Ecol Evol 14(6):224–228
Boufahja F, Sellami B, Dellali M, Aissa P, Mahmoudi E, Beyrem H (2011) A microcosm experiment on the effects of permethrin on a free-living nematode assemblage. Nematology 13:901–909
Brion D, Pelletier E (2005) Modelling PAHs adsorption and sequestration in freshwater and marine sediments. Chemosphere 61(6):867–876
Carman KR, Fleeger JW, Means JC, Pomarico SM, McMillin DJ (1995) Experimental investigation of the effects of polynuclear aromatic-hydrocarbons on an estuarine sediment food-web. Mar Environ Res 40(3):289–318
Carman KR, Fleeger JW, Pomarico SM (2000) Does historical exposure to hydrocarbon contamination alter the response of benthic communities to diesel contamination? Mar Environ Res 49(3):255–278
Cheung KC, Zhang JY, Deng HH, Ou YK, Leung HM, Wu SC, Wong MH (2008) Interaction of higher plant (jute), electrofused bacteria and mycorrhiza on anthracene biodegradation. Bioresour Technol 99(7):2148–2155
Chinnadurai G, Fernando OJ (2007) Meiofauna of mangroves of the southeast coast of India with special reference to the free-living marine nematode assemblage. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 72(1–2):329–336
Clarke KR, Warwick RM (2001) Changes in marine communities: an approach to statistical analysis and interpretation. PRIMER-E, Plymouth
Cornelissen G, Rigterink H, Ferdinandy M, V N P (1998) Rapidly desorbing fractions of PAHs in contaminated sediments as a predictor of the extent of bioremediation. Environ Sci Technol 32:966–970
Coull BC (1990) Are members of the meiofauna food for higher trophic levels. Trans Am Microsc Soc 109(3):233–246
Derouiche A, Sanda YG, Driss MR (2004) Polychlorinated biphenyls in sediments from Bizerte Lagoon, Tunisia. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 73(5):810–817
Ditoro DM, Zarba CS et al (1991) Technical basis for establishing sediment quality criteria for nonionic organic-chemicals using equilibrium partitioning. Environ Toxicol Chem 10(12):1541–1583
Erickson RJ, Ankley GT, DeFoe DL, Kosian PA, Makynen EA (1999) Additive toxicity of binary mixtures of phototoxic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to the oligochaete Lumbriculus variegatus. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 154(1):97–105
Gee JM (1989) An ecological and economic-review of meiofauna as food for fish. Zool J Linn Soc 96(3):243–261
Giere O (2009) Meiobenthology, the microscopic fauna in aquatic sediments. Springer, Berlin
Gomes V, Passos M, Leme NMP, Santos TCA, Campos DYF, Hasue FM, Phan V (2009) Photo-induced toxicity of anthracene in the Antarctic shallow water amphipod, Gondogeneia antarctica. Polar Biol 32(7):1009–1021
Goni-Urriza M, Cravo-Laureau C, Duran R (2013) Microbial Bioremediation of Aquatic Environments. In: Férard JF, Blaise C (eds) Encyclopedia of Aquatic Ecotoxicology. Springer, Dordrecht
Guo CL, Zhou HW, Wong YS, Tam NFY (2005) Isolation of PAH-degrading bacteria from mangrove sediments and their biodegradation potential. Mar Pollut Bull 51(8–12):1054–1061
Gyedu-Ababio TK, Baird D (2006) Response of meiofauna and nematode communities to increased levels of contaminants in a laboratory microcosm experiment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 63(3):443–450
Heip C, Vincx M, Vranken G (1985) The ecology of marine nematodes. Oceanogr Mar Biol 23:399–489
Hermi M, Mahmoudi E, Beyrem H, Aissa P, Essid N (2009) Responses of a free-living marine nematode community to mercury contamination: results from microcosm experiments. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 56(3):426–433
Holmer M, Forbes VE, Forbes TL (1997) Impact of the polychaete Capitella sp. I on microbial activity in an organic-rich marine sediment contaminated with the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon fluoranthene. Mar Biol 128(4):679–688
Hoss S, Claus E, Von der Ohe PC, Brinke M, Gude H, Heininger P, Traunspurger W (2011) Nematode species at risk—a metric to assess pollution in soft sediments of freshwaters. Environ Int 37(5):940–949
Jacques RJS, Okeke BC, Bento FM, Teixeira AS, Peralba MCR, Camargo FAO (2008) Microbial consortium bioaugmentation of a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons contaminated soil. Bioresour Technol 99(7):2637–2643
Juhasz AL, Naidu R (2000) Bioremediation of high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: a review of the microbial degradation of benzo[a]pyrene. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 45(1–2):57–88
Kayal S, Connell DW (1995) Polycyclic Aromatic-Hydrocarbons in Biota from the Brisbane River Estuary, Australia. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 40(5):475–493
Lambshead PJD, Platt HM, Shaw KM (1983) The detection of differences among assemblages of marine benthic species based on an assessment of dominance and diversity. J Nat Hist 17(6):859–874
Legendre P, Legendre L (1998) Numerical ecology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Lin TC, Pan PT, Young CC, Chang JS, Chang TC, Cheng SS (2011) Evaluation of the optimal strategy for ex situ bioremediation of diesel oil-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18(9):1487–1496
Losi V, Ferrero TJ, Moreno M, Gaozza L, Rovere A, Firpo M, Marques JC, Albertelli G (2013) The use of nematodes in assessing ecological conditions in shallow waters surrounding a Mediterranean harbour facility. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 130:209–221
Louati H, Ben Said O, Got P, Soltani A, Mahmoudi E, Cravo-Laureau C, Duran R, Aissa P, Pringault O (2013a) Microbial community responses to bioremediation treatments for the mitigation of low-dose anthracene in marine coastal sediments of Bizerte lagoon (Tunisia). Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:300–310
Louati H, Ben Said O, Soltani A, Got P, Mahmoudi E, Cravo-Laureau C, Duran R, Aissa P, Pringault O (2013b) The roles of biological interactions and pollutant contamination in shaping microbial benthic community structure. Chemosphere 93:2535–2546
MacRae JD, Hall KJ (1998) Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) in marine sediment under denitrifying conditions. Water Sci Technol 38(11):177–185
Mahmoudi E, Essid N, Beyrem H, Hedfi A, Boufahja F, Vitiello P, Aissa P (2005) Effects of hydrocarbon contamination on a free living marine nematode community: results from microcosm experiments. Mar Pollut Bull 50(11):1197–1204
Mahmoudi E, Essid N, Beyrem H, Hedfi A, Boufahja F, Vitiello P, Aissa P (2007) Individual and combined effects of lead and zinc on a free-living marine nematode community: results from microcosm experiments. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 343(2):217–226
Mekenyan OG, Ankley GT, Veith GD, Call DJ (1994) Qsars for photoinduced toxicity. 1. Acute lethality of polycyclic aromatic-hydrocarbons to Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 28(3):567–582
Miyasaka T, Asami H, Watanabe K (2006) Impacts of bioremediation schemes on bacterial population in naphthalene-contaminated marine sediments. Biodegradation 17(3):227–235
Narbonne JF, Djomo JE, Ribera D, Ferrier V, Garrigues P (1999) Accumulation kinetics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons adsorbed to sediment by the mollusk Corbicula fluminea. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 42(1):1–8
Naslund J, Nascimento FJA, Gunnarsson JS (2010) Meiofauna reduces bacterial mineralization of naphthalene in marine sediment. ISME J 4(11):1421–1430
Nkansah MA, Christy AA, Barth T (2011) The use of anthracene as a model compound in a comparative study of hydrous pyrolysis methods for industrial waste remediation. Chemosphere 84(4):403–408
Onwurah INE, Ogugua VN, Onyike NB, Ochonogor AE, Otitoju OF (2007) Crude oil spills in the environment, effects and some innovative clean-up biotechnologies. Int J Environ Res 1(4):307–320
Oris JT, Giesy JP (1987) The photoinduced toxicity of polycyclic aromatic-hydrocarbons to larvae of the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Chemosphere 16(7):1395–1404
Palacin C, Gili JM, Martin D (1992) Evidence for coincidence of meiofauna spatial heterogeneity with eutrophication processes in a shallow-water Mediterranean Bay. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 35(1):1–16
Perugini M, Visciano P, Giammarino A, Manera M, Di Nardo W, Amorena M (2007) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in marine organisms from the Adriatic Sea, Italy. Chemosphere 66(10):1904–1910
Platt HM, Warwick RM (1983) Free living marine nematodes. Part I. British Enoplids. Synopses of the British Fauna no 28. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Platt HM, Warwick RM (1988) Free living marine nematodes. Part II. British Chromadorids. Synopses of the British Fauna no 38. E. J. Brill, Leiden
Ramette A (2007) Multivariate analyses in microbial ecology. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 62(2):142–160
Riera P, Hubas C (2003) Trophic ecology of nematodes from various microhabitats of the Roscoff Aber Bay (France): importance of stranded macroalgae evidenced through delta C-13 and delta N-15. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 260:151–159
Roling WFM, Milner MG, Jones DM, Fratepietro F, Swannell RPJ, Daniel F, Head IM (2004) Bacterial community dynamics and hydrocarbon degradation during a field-scale evaluation of bioremediation on a mudflat beach contaminated with buried oil. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(5):2603–2613
Sese BT, Grant A, Reid BJ (2009) Toxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. J Toxicol Environ Health A 72(19):1168–1180
Smolinski A, Stanczyk K, Kapusta K, Howaniec N (2013) Analysis of the organic contaminants in the condensate produced in the in situ underground coal gasification process. Water Sci Technol 67(3):644–650
Toxnet (2003) Hazardous Substances Data Bank of Toxnet
Traczewska TM (2000) Changes of toxicological properties of biodegradation products of anthracene and phenanthrene. Water Sci Technol 41(12):31–38
Traunspurger W (1997) Bathymetric, seasonal and vertical distribution of feeding-types of nematodes in an Oligotrophic lake. Vie et Milieu Life Environ 47(1):1–7
Warwick RM, Clarke KR (1991) A comparison of some methods for analyzing changes in benthic community structure. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 71(1):225–244
Warwick RM, Platt HM, Somerfield PJ (1998) Free-living marine nematodes. Part III. British monhysterids. Synopses of the British Fauna (New Series). Studies Council, Shrewsbury
Wieser W (1960) Benthic studies in Buzzards Bay. 2. The meiofauna. Limnol Oceanogr 5(2):121–137
Yoshida M, Hamadi K, Ghrabi A (2002) Solid waste landfills and soil/sediment contamination around Bizerte lagoon: possible pollution sources. In: Ghrabi A, Yoshida M (eds) Study on environmental pollution of Bizerte lagoon. INRST-JICA Publishers, Tunis, p 55
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by funding from the CMCU program (PHC-UTIQUE, n° 09G 0189), Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD) and the Faculté des Sciences de Bizerte (FSB). Dr. Emma Rochelle-Newall is gratefully acknowledged as native English speaker for her helpful criticisms on an early version of the manuscript and for English improvements.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Louati, H., Ben Said, O., Soltani, A. et al. Impacts of bioremediation schemes for the mitigation of a low-dose anthracene contamination on free-living marine benthic nematodes. Ecotoxicology 23, 201–212 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-013-1163-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-013-1163-9