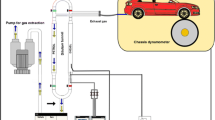
Abstract
Inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry coupled with cation exchange matrix separation has been optimised for the direct determination of platinum group element (PGE) and trace element emissions from a diesel engine car. After matrix separation method detection limits of 1.6 ng g−1 for Pd, 0.4 ng g−1 for Rh and 4.3 ng g−1 for Pt were achieved, the method was validated against the certified reference material BCR 723, urban road dust. The test vehicle was fitted with new and aged catalytic converters with and without diesel particulate filters (DPF). Samples were collected after three consecutive New European Driving Cycle (NEDC) of the particulate and “soluble” phases using a home-made sampler optimised for trace element analysis. Emission factors for the PGEs ranged from 0.021 ng km−1 for Rh to 70.5 ng km−1 for Pt; when a DPF was fitted, the emission factors for the PGEs actually used in the catalysts dropped by up to 97% (for Pt). Trace element emission factors were found to drop by a maximum of 92% for Ni to a minimum of 18% for Y when a DPF was fitted; a new DPF was also found to cause a reduction of up to 86% in the emission of particulate matter.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ek KH, Morrison GM, Rauch S (2004) Environmental routes for platinum group elements to biological materials—a review. Sci Total Environ, Elsevier Science Bv 334:21–38
Matthey J (2007) Platinum 2007 Report. Platinum, Hertfordshire, UK
Bencs L, Ravindra K, Van Grieken R (2003) Methods for the determination of platinum group elements originating from the abrasion of automotive catalytic converters. Spectrochim Acta B 58(10):1723–1755
Barbante C, Veysseyre A, Ferrari C, Van de Velde K, Morel C, Capodaglio G, Cescon P, Scarponi G, Boutron C (2001) Greenland snow evidence of large scale atmospheric contamination for platinum, palladium, and rhodium. Environ Sci Technol 35(5):835–839
Rauch S, Hemond HF (2003) Sediment-based evidence of platinum concentration changes in an urban lake near Boston, Massachusetts. Environ Sci Technol 37(15):3283–3288
Moldovan M, Palacios MA, Gomez MM, Morrison G, Rauch S, McLeod C, Ma R, Caroli S, Alimonti A, Petrucci F, Bocca B, Schramel P, Zischka M, Pettersson C, Wass U, Luna M, Saenz JC, Santamaria J (2002) Environmental risk of particulate and soluble platinum group elements released from gasoline and diesel engine catalytic converters. Sci Total Environ 296(1–3):199–208
Ravindra K, Bencs L, Van Grieken R (2004) Platinum group elements in the environment and their health risk. Sci Total Environ 318(1–3):1–43
Schafer J, Hannker D, Eckhardt JD, Stuben D (1998) Uptake of traffic-related heavy metals and platinum group elements (PGE) by plants. Sci Total Environ 215(1–2):59–67
Sures B, Zimmermann S, Messerschmidt J, von Bohlen A, Alt F (2001) First report on the uptake of automobile catalyst emitted palladium by European eels (Anguilla anguilla) following experimental exposure to road dust. Environ Pollut 113(3):341–345
Schins RPF, Polat D, Begerow J, Turfeld M, Becker A, Borm PJA (2004) Platinum levels in nasal lavage fluid as a biomarker for traffic-related exposure and inflammation in children. Sci Total Environ 334−335:447–455
Bartholomew CH, Farrauto RJ (2005) Fundamentals of industrial catalytic processes, 2nd edn. Wiley, Hoboken, NJ
Pope CA, Burnett RT, Thun MJ, Calle EE, Krewski D, Ito K, Thurston GD (2002) Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. JAMA, J Am Med Assoc 287(9):1132–1141
DieselNet DieselNet: emission standards, European union, cars and light trucks. http://www.dieselnet.com/standards/eu/ld.php
Twigg MV, Phillips PR (2009) Cleaning the air we breathe—controlling diesel particulate emissions from passenger cars. Platinum Met Rev 53(1):27–34
Johnson TV (2009) Review of diesel emissions and control. Int J Engine Res 10(5):275–285
Hu SH, Herner JD, Shafer M, Robertson W, Schauer JJ, Dwyer H, Collins J, Huai T, Ayala A (2009) Metals emitted from heavy-duty diesel vehicles equipped with advanced PM and NOX emission controls. Atmos Environ 43(18):2950–2959
Cheung KL, Ntziachristos L, Tzamkiozis T, Schauer JJ, Samaras Z, Moore KF, Sioutas C (2010) Emissions of particulate trace elements, metals and organic species from gasoline, diesel, and biodiesel passenger vehicles and their relation to oxidative potential. Aerosol Sci Technol 44(7):500–513
Moldovan M, Gomez MM, Palacios MA (1999) Determination of platinum, rhodium and palladium in car exhaust fumes. J Anal At Spectrom 14(8):1163–1169
Hann S, Koellensperger G, Kanitsar K, Stingeder G (2001) ICP-SFMS determination of palladium using IDMS in combination with on-line and off-line matrix separation. J Anal At Spectrom 16(9):1057–1063
Mukai H, Ambe Y, Morita M (1990) Flow-injection inductively coupled plasma mass-spectrometry for the determination of platinum in airborne particulate matter. J Anal At Spectrom 5(1):75–80
Ely JC, Neal CR, O'Neill JA, Jain JC (1999) Quantifying the platinum group elements (PGEs) and gold in geological samples using cation exchange pretreatment and ultrasonic nebulization inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (USN-ICP-MS). Chem Geol 157(3–4):219–234
Palacios M, Gomez MM, Moldovan M, Morrison G, Rauch S, McLeod C, Ma R, Laserna J, Lucena P, Caroli S, Alimonti A, Petrucci F, Bocca B, Schramel P, Lustig S, Zischka M, Wass U, Stenbom B, Luna M, Saenz JC, Santamaria J (2000) Platinum-group elements: quantification in collected exhaust fumes and studies of catalyst surfaces. Sci Total Environ 257(1):1–15
Toscano G, Gambaro A, Capodaglio G, Cairns WRL, Cescon P (2009) Assessment of a procedure to determine trace and major elements in atmospheric aerosol. J Environ Monit 11(1):193–199
Stortini AM, Freda A, Cesari D, Cairns WRL, Contini D, Barbante C, Prodi F, Cescon P, Gambaro A (2009) An evaluation of the PM2.5 trace elemental composition in the Venice Lagoon area and an analysis of the possible sources. Atmos Environ 43(40):6296–6304
Rauch S, Morrison GM, Moldovan M (2002) Scanning laser ablation-ICP-MS tracking of platinum group elements in urban particles. Sci Total Environ 286(1–3):243–251
Moldovan M, Rauch S, Morrison GM, Gomez M, Palacios MA (2003) Impact of ageing on the distribution of platinum group elements and catalyst poisoning elements in automobile catalysts. Surf Interface Anal 35(4):354–359
Dwyer H, Ayala A, Zhang S, Collins J, Huai T, Herner J, Chau W (2010) A study of emissions from a Euro 4 light duty diesel vehicle with the European particulate measurement programme. Atmos Environ 44(29):3469–3476
Wagner A, Boman J, Gatari MJ (2008) Elemental analysis of size-fractionated particulate matter sampled in Goteborg, Sweden. Spectrochim Acta B 63(12):1426–1431
Witt MLI, Meheran N, Mather TA, de Hoog JCM, Pyle DM (2010) Aerosol trace metals, particle morphology and total gaseous mercury in the atmosphere of Oxford, UK. Atmos Environ 44(12):1524–1538
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Italian Ministry of Instruction, University and Research (MIUR) for funding the PhD of Antonella De Boni through the 2004 Fund for Young Researchers on the topic: Innovative Chemical Processes. We would also like to thank The French Environment and Energy Control Agency, ADEME (Agence de l'Environnement et de la Maîtrise de l' Energie), for financing this work. The authors also gratefully acknowledge the help of ELGA LabWater in providing the PURELAB Option-R and Ultra Analytic, which produced the ultra-pure water used in these experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in the special issue on Advances in Analytical Mass Spectrometry with Guest Editor Maria Careri.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cairns, W.R.L., De Boni, A., Cozzi, G. et al. The use of cation exchange matrix separation coupled with ICP-MS to directly determine platinum group element (PGE) and other trace element emissions from passenger cars equipped with diesel particulate filters (DPF). Anal Bioanal Chem 399, 2731–2740 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-4596-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-4596-5