Abstract
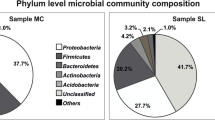
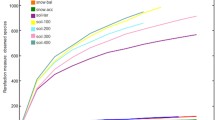
16S rRNA gene (rrs) clone libraries were constructed from two snow samples (May 11, 2007 and June 7, 2007) and two meltwater samples collected during the spring of 2007 in Svalbard, Norway (79°N). The libraries covered 19 different microbial classes, including Betaproteobacteria (21.3%), Sphingobacteria (16.4%), Flavobacteria (9.0%), Acidobacteria (7.7%) and Alphaproteobacteria (6.5%). Significant differences were detected between the two sets of sample libraries. First, the meltwater libraries had the highest community richness (Chao1: 103.2 and 152.2) and Shannon biodiversity indices (between 3.38 and 3.59), when compared with the snow libraries (Chao1: 14.8 and 59.7; Shannon index: 1.93 and 3.01). Second, ∫-LIBSHUFF analyses determined that the bacterial communities in the snow libraries were significantly different from those of the meltwater libraries. Despite these differences, our data also support the theory that a common core group of microbial populations exist within a variety of cryohabitats.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amato P et al (2007) Bacterial characterization of the snow cover at Spitzberg, Svalbard. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 59:255–264
Barkay T, Poulain AJ (2007) Mercury (micro) biogeochemistry in polar environments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 59:232–241
Brinkmeyer R, Knittel K, Jurgens J, Weyland H, Amann R, Helmke E (2003) Diversity and structure of bacterial communities in Arctic versus Antarctic pack ice. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:6610–6619
Carpenter EJ, Lin S, Capone DG (2000) Bacterial activity in South Pole snow. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:4514–4517
Chao A (1984) Non-parametric estimation of the number of classes in a population. Scand J Stat 11:265–270
Chauhan S, Shivaji S (1994) Growth and pigmentation in Sphingobacterium antarcticus, a psychotropic bacterium from Antarctica. Polar Biol 14:31–36
Cheng SM, Foght JM (2007) Cultivation-independent and -dependent characterization of Bacteria resident beneath John Evans Glacier. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 59:318–330
Christner BC, Mosley-Thompson E, Thompson LG, Zagorodnov VS, Sandman K, Reeve JN (2000) Recovery and identification of viable bacteria immured in glacial ice. Icarus 144:479–485
Christner BC, Mosley-Thompson E, Thompson LG, Reeve JN (2001) Isolation of bacteria and 16S rDNAs from Lake Vostok accretion ice. Environ Microbiol 3:570–577
Cole JR et al (2003) The ribosomal database project (RDP-II): previewing a new autoaligner that allows regular updates and the new prokaryotic taxonomy. Nucleic Acids Res 31:442–443
Cole JR et al (2009) The ribosomal database project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 37:Database Issue D141–D145. doi:110.1093/nar/gkn1879
David MM, Mesle M, Malandain C, Cohen D, Vogel TM (2009) Molecular biology-based strategy for site remediation. Env Sci Technol (submitted)
Good IL (1953) The population frequencies of species and the estimation of population parameters. Biometrika 40:237–264
Hodson A et al (2008) Glacial ecosystems. Ecol Monogr 78:41–67
Hoham RW (1975) Optimal temperatures and temperature ranges for growth of snow algae. Arct Alp Res 7:13–24
Hoham RW, Duval B (2001) Microbial ecology of snow and freshwater ice with emphasis on snow algae. In: Jones HG, Pomeroy JW, Walker DA, Hoham RW (eds) Snow ecology: an interdisciplinary examination of snow-covered ecosystems. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 168–228
Hughes JB, Hellmann JJ, Ricketts TH, Bohannan BJM (2001) Counting the uncountable: statistical approaches to estimating microbial diversity. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4399–4406
Jones HG (1999) The ecology of snow-covered systems: a brief overview of nutrient cycling and life in the cold. Hydrol Process 13:2135–2147
Jones RT, Robeson MS, Lauber CL, Hamady M, Knight R, Fierer N (2009) A comprehensive survey of soil acidobacterial diversity using pyrosequencing and clone library analyses. Isme J 3:442–453
Jukes TH, Cantor CR (1969) Evolution of protein molecules. In: Munro HN (ed) Mammalian protein metabolism. Academic Press, New York, pp 21–132
Kemp PF, Aller JY (2004) Bacterial diversity in aquatic and other environments: what 16S rDNA libraries can tell us. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 47:161–177
Kuhn M (2001) The nutrient cycle through snow and ice, a review. Aquat Sci 63:150–167
Liu Y, Yao T, Jiao N, Kang S, Zeng Y, Huang S (2006) Microbial community structure in moraine lakes and glacial meltwaters, Mount Everest. FEMS Microbiol Lett 265:98–105
Liu Y et al (2009) Bacterial diversity in the snow over Tibetan Plateau Glaciers. Extremophiles 13:411–423
Magurran AE (1988) Ecological diversity and its measurement. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Miteva V (2007) Bacteria in snow and glacier ice. In: Margesin R, Schinner F, Marx JC, Gerday C (eds) Psychrophiles: from biodiversity to biotechnology. Springer, Berlin, pp 31–50
Miwa T (1975) Clostridia in soil of the Antarctica. Jpn J Med Sci Biol 28:201–213
Perrière G, Gouy M (1996) WWW-Query: an on-line retrieval system for biological sequence banks. Biochimie 78:364–369
Pettitt AN (1982) Cramér-von Mises statistic. In: Kotz S, Johnson NL, Read CB (eds) Encyclopedia of statistical sciences. Wiley, New York, pp 220–221
Poulain AJ et al (2007) Potential for mercury reduction by microbes in the high arctic. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:2230–2238
Priscu JC, Christner BC (2004) Earth’s icy biosphere. In: Bull AT (ed) Microbial diversity and bioprospecting. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 130–145
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Schloss PD, Handelsman J (2005) Introducing DOTUR, a computer program for defining operational taxonomic units and estimating species richness. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1501–1506
Schloss PD, Larget BR, Handelsman J (2004) Integration of microbial ecology and statistics: a test to compare gene libraries. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:5485–5492
Segawa T, Miyamoto K, Ushida K, Agata K, Okada N, Kohshima S (2005) Seasonal change in bacterial flora and biomass in mountain snow from the Tateyama Mountains, Japan, analyzed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing and real-time PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:123–130
Skidmore ML, Foght JM, Sharp MJ (2000) Microbial life beneath a high arctic glacier. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3214–3220
Skidmore M, Anderson SP, Sharp M, Foght J, Lanoil BD (2005) Comparison of microbial community compositions of two subglacial environments reveals a possible role for microbes in chemical weathering processes. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:6986–6997
Spring S, Merkhoffer B, Weiss N, Kroppenstedt RM, Hippe H, Stackebrandt E (2003) Characterization of novel psychrophilic clostridia from an Antarctic microbial mat: description of Clostridium frigoris sp. nov., Clostridium lacusfryxellense sp. nov., Clostridium bowmanii sp. nov. and Clostridium psychrophilum sp. nov. and reclassification of Clostridium laramiense as Clostridium estertheticum subsp. laramiense subsp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:1019–1029
Stackebrandt E, Brambilla E, Cousin S, Dirks W, Pukall R (2004) Culture-independent analysis of bacterial species from an anaerobic mat from Lake Fryxell, Antarctica: prokaryotic diversity revisited. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 50:517–524
Stibal M, Elster J, Sabacka M, Kastovska K (2007) Seasonal and diel changes in photosynthetic activity of the snow alga Chlamydomonas nivalis (Chlorophyceae) from Svalbard determined by pulse amplitude modulation fluorometry. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 59:265–273
Thomas WH, Duval B (1995) Sierra Nevada, California, USA, snow algae: snow albedo changes, algal-bacterial interrelationships, and ultraviolet radiation effects. Arct Alp Res 27:389–399
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 24:4876–4882
Tranter M, Sharp MJ, Lamb HR, Brown GH, Hubbard BP, Willis IC (2002) Geochemical weathering at the bed of Haut Glacier d’Arolla, Switzerland—a new model. Hydrol Process 16:959–993
Ward DM, Weller R, Bateson MM (1990) 16S rRNA sequences reveal numerous uncultured microorganisms in a natural community. Nature 345:63–65
Yao TD, Xiang SR, Zhang XJ, Wang NL, Wang YQ (2006) Microorganisms in the Malan ice core and their relation to climatic and environmental changes. Global Biogeochem Cycles 20:GB1004. doi:1010.1029/2004GB002424
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the three anonymous reviewers that went over the manuscript. The authors would like to acknowledge the contribution of Cédric Couret and the entire AWIPEV staff, Xavier Faïn and Jean Philippe Balestrieri. This research was supported by grants from EC2CO/CYTRIX (Programme National INSU), LEFE, IPEV CHIMERPOL program (399) and CL would like to acknowledge the FQRNT (le Fonds Québécois de la Recherche sur la Nature et les Technologies) for a PhD research fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by T. Matsunaga.
D. Schneider and T. M. Vogel contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larose, C., Berger, S., Ferrari, C. et al. Microbial sequences retrieved from environmental samples from seasonal Arctic snow and meltwater from Svalbard, Norway. Extremophiles 14, 205–212 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-009-0299-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-009-0299-2